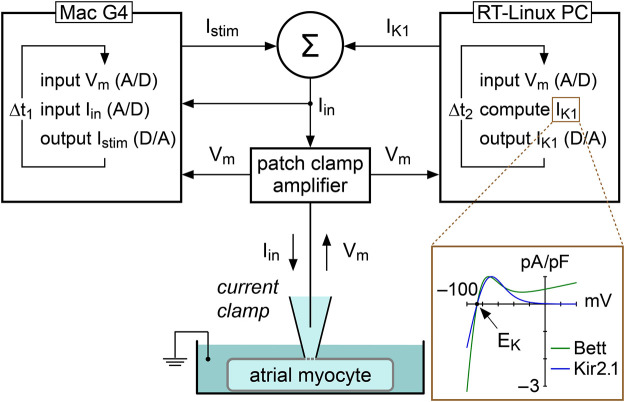
FIGURE 1.
Experimental approach to supply a patched atrial myocyte with a synthetic inward rectifier K+ current (IK1). A Real-Time Linux (RT-Linux) based PC computes the synthetic IK1 according to the membrane potential (Vm) that is read into the PC. After addition of any stimulus current (Istim), this IK1 is sent to the patch clamp amplifier, which operates in current clamp mode and injects the net current (Iin) into the patched myocyte. This process is updated with a time step Δt2 of 40 µs. Istim is sent out by the Apple Macintosh (Mac) G4 computer that is used to control the experiment and record both Vm and Iin at a rate of 40 kHz, corresponding with a time step Δt1 of 25 µs. Inset: current–voltage relationship of the synthetic IK1 with moderate rectification (“Bett” current; Bett et al., 2013) and the synthetic IK1 with strong rectification (“Kir2.1” current; Meijer van Putten et al., 2015). EK denotes the potassium equilibrium potential.