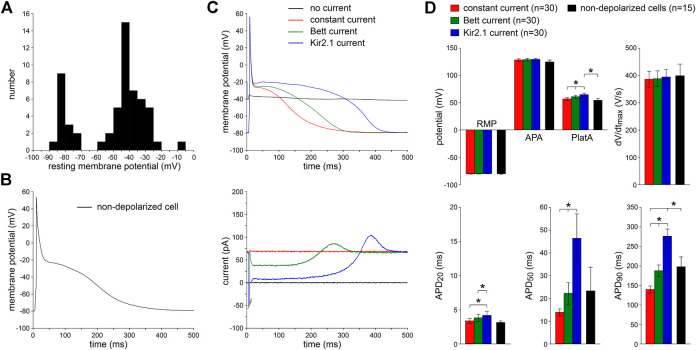
FIGURE 2.
Effects of injection of constant repolarizing current or synthetic IK1 (with moderate or strong rectification, supplied through dynamic clamp) on action potentials of enzymatically isolated human atrial myocytes. (A) Resting membrane potential (RMP) of 58 human atrial myocytes in absence of repolarizing current injection. Note the group of 15 non-depolarized myocytes (leftmost group of bars) with an RMP of −70 mV or more negative. (B) Typical action potential (AP), elicited at 1 Hz, of a non-depolarized myocyte in absence of any repolarizing current injection. (C) Top: typical APs elicited at 1 Hz in presence of injected constant or IK1 current within one originally depolarized cell (with an original RMP near −40 mV). Bottom: associated injected currents. Synthetic IK1 supplied as detailed in Figure 1. (D) Average AP parameters of 30 originally depolarized myocytes during constant current and IK1 injections with dynamic clamp. Non-depolarized cells are the 15 cells of panel A with an RMP of −70 mV or more negative in absence of any repolarizing current injection. APA, AP amplitude; PlatA, amplitude of the AP plateau; dV/dtmax, maximum AP upstroke velocity; APD20, APD50, and APD90, AP duration at 20, 50, and 90% repolarization, respectively. *p < 0.05.