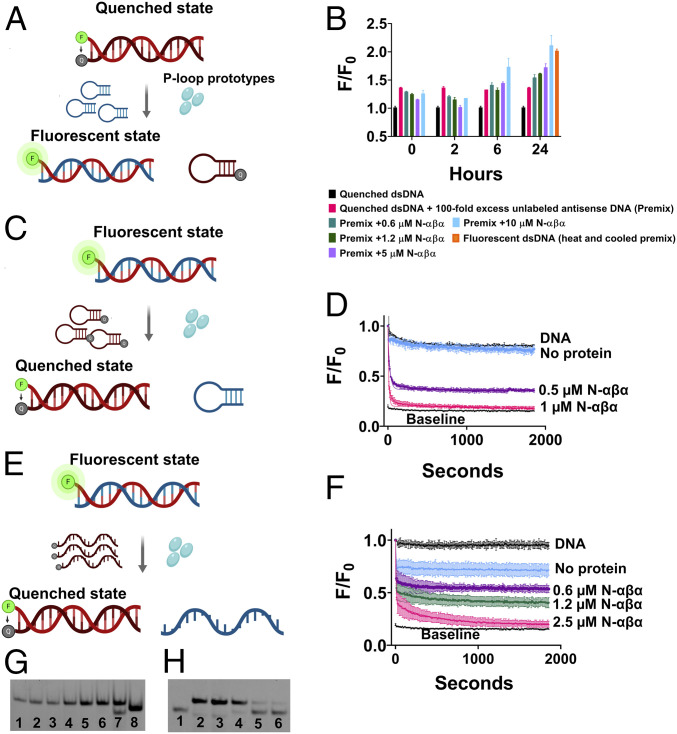
Fig. 3.
The N-αβα P-loop prototype mediates strand exchanges. (A) A schematic of the strand exchange reaction between a quenched dsDNA and a nonlabeled complementary strand (hairpin-forming). (B) The exchange reaction was monitored by increase in fluorescence upon addition of N-αβα to a premix of quenched dsDNA and 100-fold excess of unlabeled complementary antisense strand. Fluorescence was normalized (F/F0) to quenched dsDNA (equals 1) and plotted versus time (n = 2 to 4; error bars represent SD values). (C) A schematic of the strand exchange reaction between a fluorescent dsDNA and a quencher-containing complementary strand (hairpin-forming). (D) Fluorescence quenching (F/F0) was monitored upon addition of N-αβα to a premix of fluorescently labeled dsDNA and 10-fold excess of a quencher-containing competing strand (hairpin-forming) (n = 2 to 4; error bars represent SD values). Data were fit to a one-phase exponential decay (SI Appendix, Table S8). (E) A schematic of the strand exchange reaction between a fluorescent dsDNA and a quencher-containing complementary strand (linear). (F) Fluorescence quenching (F/F0) was monitored upon addition of N-αβα to a premix of fluorescently labeled dsDNA and 10-fold excess of a linear quencher-containing competing strand (n = 2; error bars represent SD values). Data were fit to a two-phase exponential decay. (G) Native EMSA gel of the strand-exchange reaction shown in B. The reactions were allowed to reach completion (24 h) and DNA products were resolved on native polyacrylamide TBE gels (see Materials and Methods). The lanes are as follows: 1) Quenched dsDNA (FAM-GA sense strand plus BHQ-1 antisense strand); 2) DNA Premix (quenched dsDNA with 100-fold excess of unlabeled antisense strand); 3 through 6) DNA Premix with N-αβα (0.6, 1.2, 5, and 10 µM, respectively); 7) Fluorescent beacon dsDNA; 8) Fluorescent ssDNA (FAM-GA sense strand) (SI Appendix, Table S1). Short dsDNA duplexes comprising of A/T rich regions are prone to improper annealing and/or formation of internal hairpins due to self-complementary regions. This is likely the reason for the visible lower band in lane 7. (H) Native EMSA gel of a strand-exchange reaction as shown in E but with both strands fluorescently labeled. Strand-exchange reactions were carried out as described above, allowed to reach steady state (14 h), and analyzed on a native polyacrylamide TBE gel. The lanes are as follows: 1) Fluorescent ssDNA (FAM-TC-linear antisense strand); 2) Fluorescent dsDNA (FAM-GA-linear sense strand plus FAM-TC-linear antisense strand); 3) DNA premix (fluorescent dsDNA with 10-fold excess of BHQ-1-linear antisense strand); 4) DNA Premix with 0.6 µM N-αβα and 5) with 1.25 µM N-αβα; 6) Quenched dsDNA (FAM-GA-linear sense strand plus BHQ-1-linear antisense strand) with FAM-TC-linear antisense strand (5 nM; 1:1 ratio).