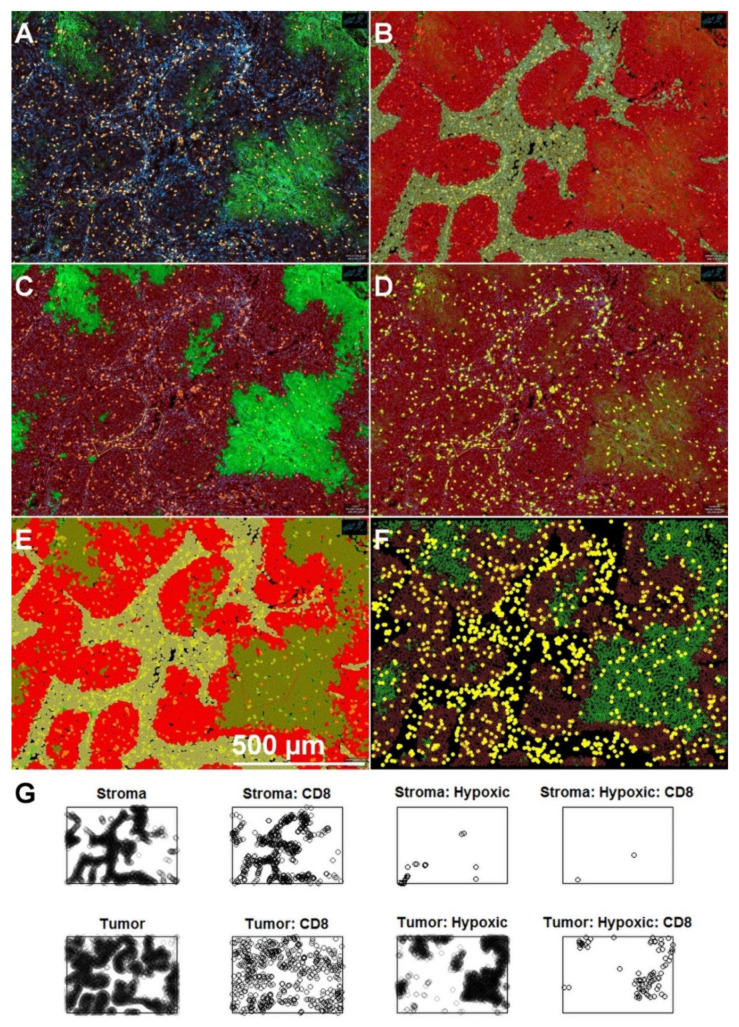
Figure 1.
A representative area from a whole-slide specimen is shown to demonstrate the procedure of data acquisition in QuPath, cell classification, and transfer to R. (A) Tumor section after single-cell detection in QuPath. Approximated cell borders, extrapolated from the positions of cell nuclei, which had been segmented based on the DAPI channel (blue), are depicted by red lines. CD8-positive cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) are shown in yellow. Hypoxic, CA IX-positive tumor cells are shown in green. (B) Result of the tumor-stroma classification using QuPath’s machine learning features. A set of example areas for tumor and stroma were delineated by the user. QuPath was then able to discriminate between both compartments for the rest of the cells in the specimen. (C,D) Construction of additional single-threshold classifiers for hypoxic cells (C) and CD8-positive CTL (D). (E) A compound classifier comprising tumor, stroma, and subclassifications according to the single-measurement classifiers shown in panels (C,D). Scale bar in (E) applies to panels A–E. (F) A color-coded plot of cell positions generated in R after transfer of the data and conversion to a multitype planar point pattern (ppp) in Spatstat. For the sake of clarity, subclassifications have been reorganized to CD8-positive CTL (yellow), normoxic tumor cells (brown), and hypoxic tumor cells (green). Original subclassifications are shown in panel (G).