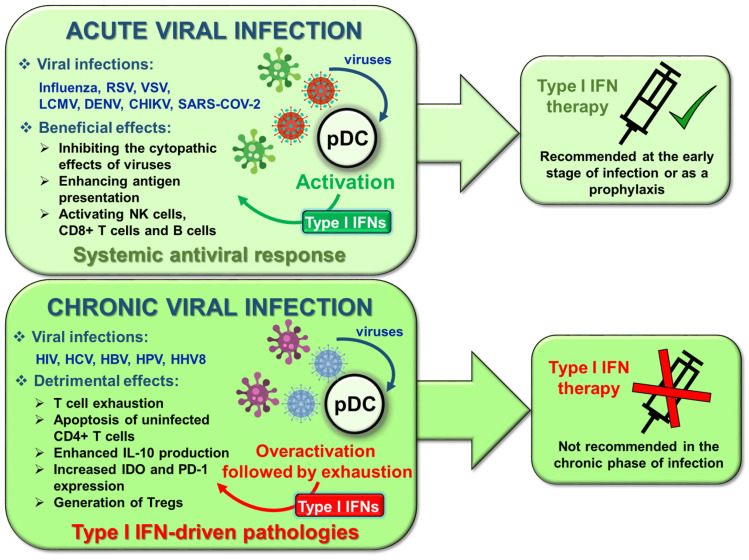
Figure 2.
The Janus-faced role of pDCs in viral infections. Via producing large amounts of type I IFNs, pDCs are essential to initiate an effective antiviral response. Recombinant type I IFN therapy is suggested for the treatment of acute viral respiratory tract infections or as a prophylaxis (upper panel). On the contrary, persistent and uncontrolled activation of pDCs leads to type I IFN-driven pathologies upon chronic viral infections. Therefore, the use of type I IFNs is not recommended for the treatment of chronic viral infections as it may exacerbate pre-existing inflammation (lower panel). CHIKV: chikungunya virus; DENV: dengue virus; HBV: hepatitis B virus; HCV: hepatitis C virus; HHV8: human herpesvirus 8; HIV: human immunodeficiency virus; HPV: human papillomavirus; IDO: indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase; IFN: interferon; IL: interleukin; LCMV: lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus; NK: natural killer; PD-1: programmed cell death protein 1; pDC: plasmacytoid dendritic cell; RSV: respiratory syncytial virus; SARS-COV-2: severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; VSV: vesicular stomatitis virus.