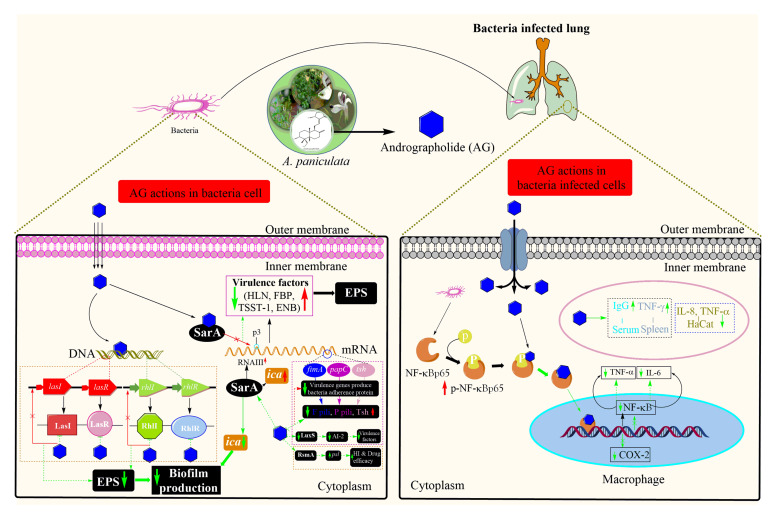
Figure 5.
Schematic representation of a plausible mechanism of actions of andrographolide in bacteria, mainly Staphylococcus aureus. AG: andrographolide ( ), the Black arrow (
), the Black arrow ( ): regular process/pathway, Black dotted rectangle area: AG Induction of Salmonella-specific cell-mediated immune response in Salmonella typhimurum, Blue dotted rectangle area: AG inhibits cellular inflammatory factor in Propionibacterium acnes, COX-2: Cyclooxygenase-2, ENB: Enterotoxin B, FBP: Fibronectin-binding protein, Green dotted arrow (
): regular process/pathway, Black dotted rectangle area: AG Induction of Salmonella-specific cell-mediated immune response in Salmonella typhimurum, Blue dotted rectangle area: AG inhibits cellular inflammatory factor in Propionibacterium acnes, COX-2: Cyclooxygenase-2, ENB: Enterotoxin B, FBP: Fibronectin-binding protein, Green dotted arrow ( ): expected regulation process, Green dotted arrow with a flat bottom (
): expected regulation process, Green dotted arrow with a flat bottom ( ): attachment of AG to the target site, Green down arrow (
): attachment of AG to the target site, Green down arrow ( ): downregulation and expected outcomes, Green up arrow (
): downregulation and expected outcomes, Green up arrow ( ): upregulation and expected outcomes, HaCaT: Human Epidermal Keratinocyte line, HLN: Hemolysin, IFN-γ: Interferon-gamma, IgG: Immunoglobulin G, IL-6: Interleukin 6, IL-8: Interleukin 8, NF-κB: Nuclear factor-kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cell, Orange dotted rectangle area: AG analogue influences the quorum sensing system and inhibits exopolysaccharides generation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. psl production is also significantly inhibited in this biofilm-forming bacteria, (
): upregulation and expected outcomes, HaCaT: Human Epidermal Keratinocyte line, HLN: Hemolysin, IFN-γ: Interferon-gamma, IgG: Immunoglobulin G, IL-6: Interleukin 6, IL-8: Interleukin 8, NF-κB: Nuclear factor-kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cell, Orange dotted rectangle area: AG analogue influences the quorum sensing system and inhibits exopolysaccharides generation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. psl production is also significantly inhibited in this biofilm-forming bacteria, ( ): Phosphorylation, Purple dotted rectangle area: AG influences quorum sensing system and reduces the expression of F1 pili, P pili and Tsh by downregulating fimA, papC and tsh in Escherichia coli. All these virulence genes help bacteria to the adherence cell surface. The red arrow (
): Phosphorylation, Purple dotted rectangle area: AG influences quorum sensing system and reduces the expression of F1 pili, P pili and Tsh by downregulating fimA, papC and tsh in Escherichia coli. All these virulence genes help bacteria to the adherence cell surface. The red arrow ( ): Inhibition/downregulation of the process, Red up arrow (
): Inhibition/downregulation of the process, Red up arrow ( ): upregulation (at disease or infection stage), TNF-α: Tumor Necrosis Factor- alpha, TSST-1: Toxic Shock Syndrome Toxin-1.
): upregulation (at disease or infection stage), TNF-α: Tumor Necrosis Factor- alpha, TSST-1: Toxic Shock Syndrome Toxin-1.