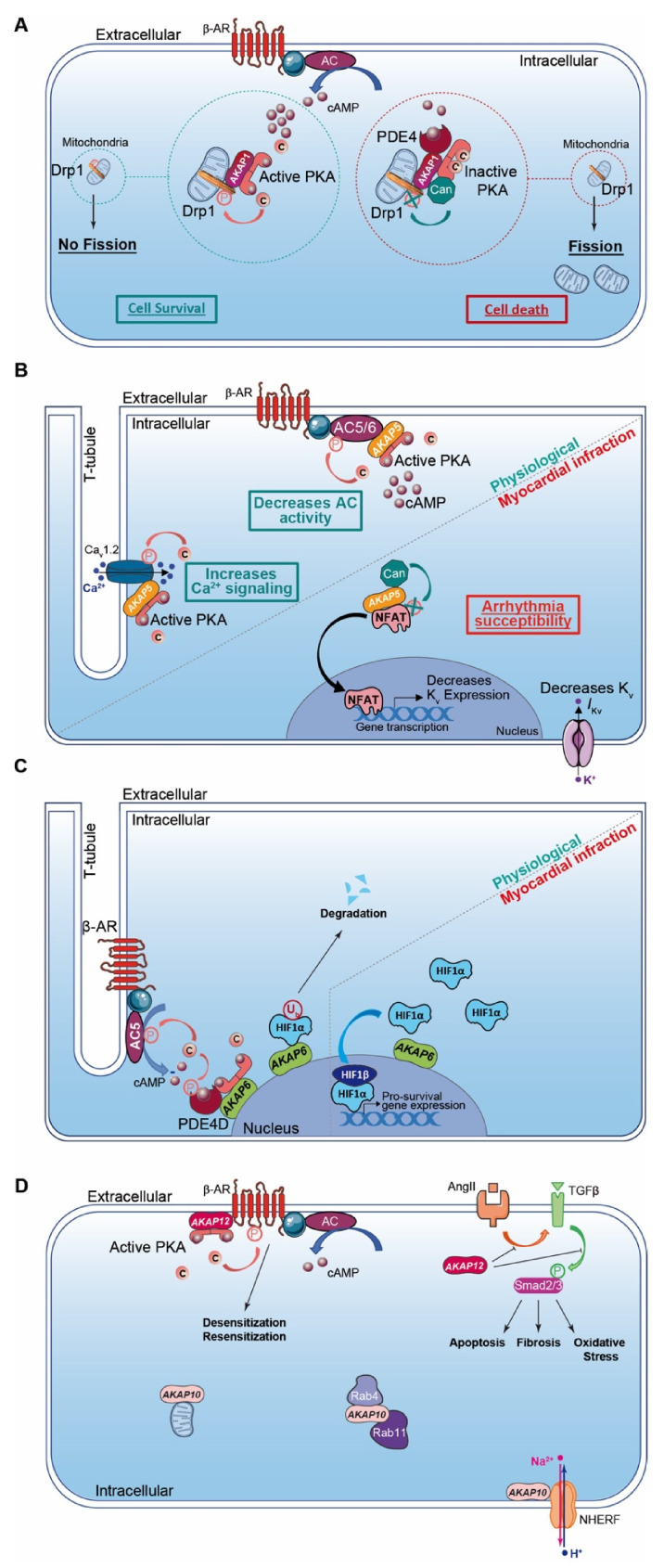
Figure 2.
Cardiac AKAPs and cAMP signaling compartmentalization in myocardial infarction (MI). (A) AKAP1 coordinates at the mitochondria a cardioprotective macrocomplex that mediates phosphorylation of Drp1 by anchored PKA, which inhibits mitochondrial fission and leads to cell survival (left). This process is counterbalanced by CaN recruitment on AKAP1 signaling complex, which, in contrast, favors Drp1 dephosphorylation and mitochondrial fragmentation (right). (B) Role of cardiac AKAP5 under physiological conditions and after MI. In cardiomyocytes, AKAP5-anchored PKA mediates direct AC5 and AC6 phosphorylation to inhibit AC activity and cAMP production (top left). AKAP5 brings PKA in proximity to LTCC, which regulates Ca2+ entry (bottom left). AKAP5 anchors CaN and participates in NFATc3 activation, which down-regulates Kv channel expression level, reduces IKv, prolongs action potential duration and favors arrhythmia susceptibility post-MI (right). (C) Role of cardiac AKAP6 under physiological conditions and after MI. Activated AC5 produces a pool of cAMP that mobilizes AKAP6-anchored PKA. PKA phosphorylates AC5 and AKAP6-anchored PDE4D that, respectively, inhibit AC5-dependent cAMP production and trigger local cAMP degradation by PDE4D (left). Under physiological conditions, AKAP6 mediates HIF1-α ubiquitination and degradation, while hypoxia inhibits this process and leads to HIF1-α accumulation. HIF1-α complexes with HIF1-β and initiates transcription of pro-survival genes to favor cell survival under ischemic stress (right). (D) Cardiac AKAP10 and AKAP12 under physiological conditions. In the heart, AKAP10 distributes to the mitochondria, in the cytoplasm (with small GTPases Rab4 and Rab11) and at the plasmalemma (associated with Na/H exchanger (NHERF)). AKAP12 favors β-AR phosphorylation and triggers GPCR desensitization/resensitization cycling. In the heart, angiotensin II (AngII) activates cardiac TGFβ1 pathways, which favors oxidative stress, apoptosis and fibrosis. AKAP12 inhibits deleterious AngII and the TGFβ1 pathway and exhibits cardioprotective properties. AKAP: A-kinase anchoring protein; HIF1α: Hypoxia Induced Factor-1α; CaN: calcineurin; PDE4: phosphodiesterase 4; AC5/6: adenylyl cyclase 5/6; β-AR: β-Adrenergic Receptor.