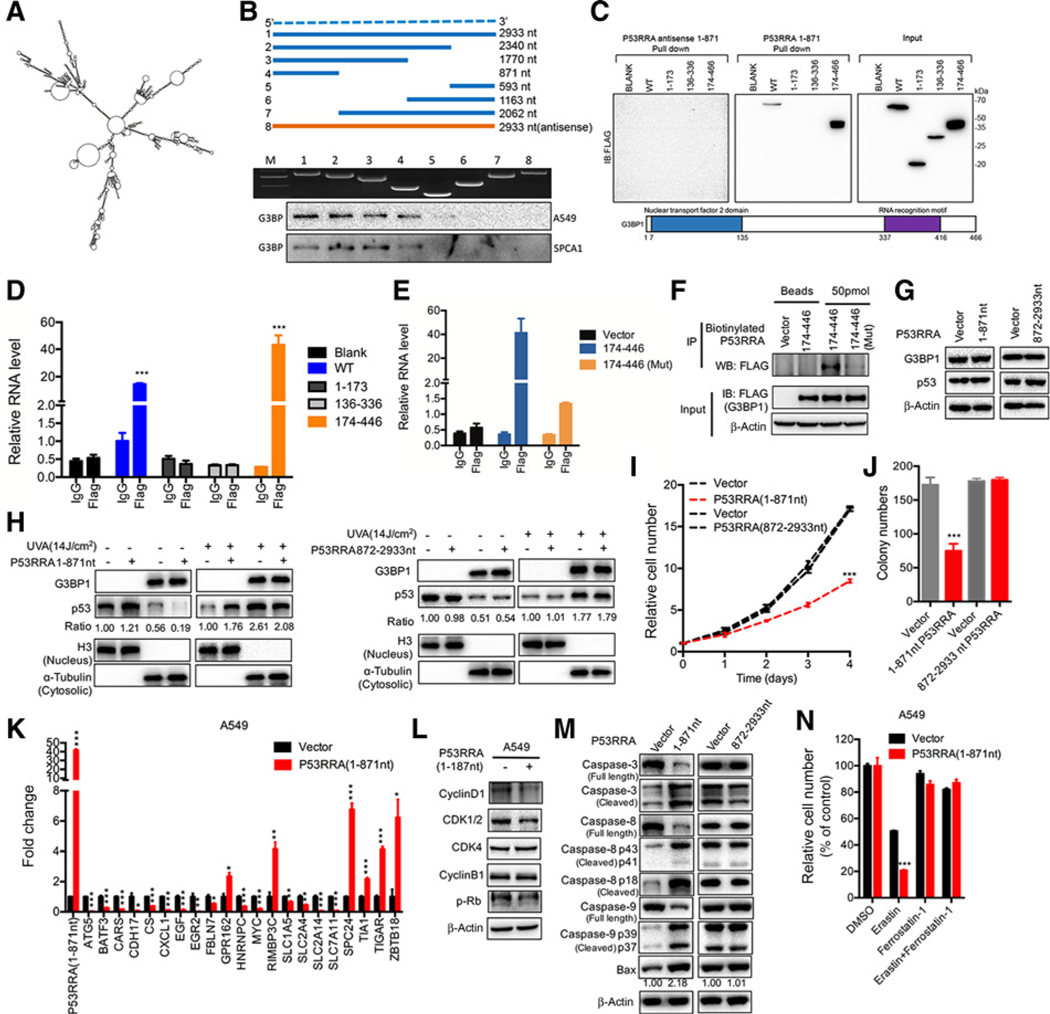
Figure 7.
The 1–187 nt of P53RRA interacts with the G3BP1 RRM domain via residues critical to RNA binding, inhibiting cell growth and affecting target gene expression, cell cycle, and apoptosis. A, The predicted secondary structure of P53RRA. B, Deletion mapping of the G3BP1-binding domain in P53RRA. Top, diagrams of full-length P53RRA and the deletion fragments. Middle, the in vitro–transcribed full-length P53RRA and deletion fragments with the correct sizes are indicated. Bottom, immunoblot analysis for G3BP1 in the protein samples pulled down by different P53RRA constructs. C, The immunoblot analysis of FLAG-tagged G3BP1 [wild-type (WT) vs. domain truncation mutants] retrieved by in vitro–transcribed biotinylated P53RRA. The domain structure of G3BP1 is shown below. D, RIP assays show the association of the G3BP1 RRM domain with P53RRA. E, The isolated G3BP1 RRM domain is sufficient for binding to P53RRA, as demonstrated using the RIP-assay. F, RIP assays using biotinylated P53RRA indicated that P53RRA interacted with the G3BP1 RRM domain via residues critical to RNA binding. G, Overexpression of truncated in A549 cells did not change G3BP1 and p53 protein levels. H, p53 was sequestered in the nucleus in the presence of 1–871 nt of P53RRA, whereas UVA treatment induced greater accumulation of p53 in the cytoplasm. I and J, MTT assays (I) and plate colony formation assays (J) were used to assess A549 cells that were stably transfected with 1–871 nt of P53RRA and 872–2933 nt of P53RRA. K, The RNA expression of genes was measured by qPCR in A549 cells overexpressing 1–187 nt of P53RRA. L, The effect of 1–187 nt P53RRA on the regulators of cell-cycle progression in A549 cells. M, The truncation 1–187 nt of P53RRA in A549 cells affected the activities of caspase-3, caspase-8, and caspase-9 in HBE cells. N, The truncation 1–187 nt of P53RRA in A549 cells in response to erastin (5 μmol/L) ± ferrostatin-1 (1 μmol/L). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.