Figure 4. The structured diversity of midbrain dopamine neurons is consistent with distributional RL.
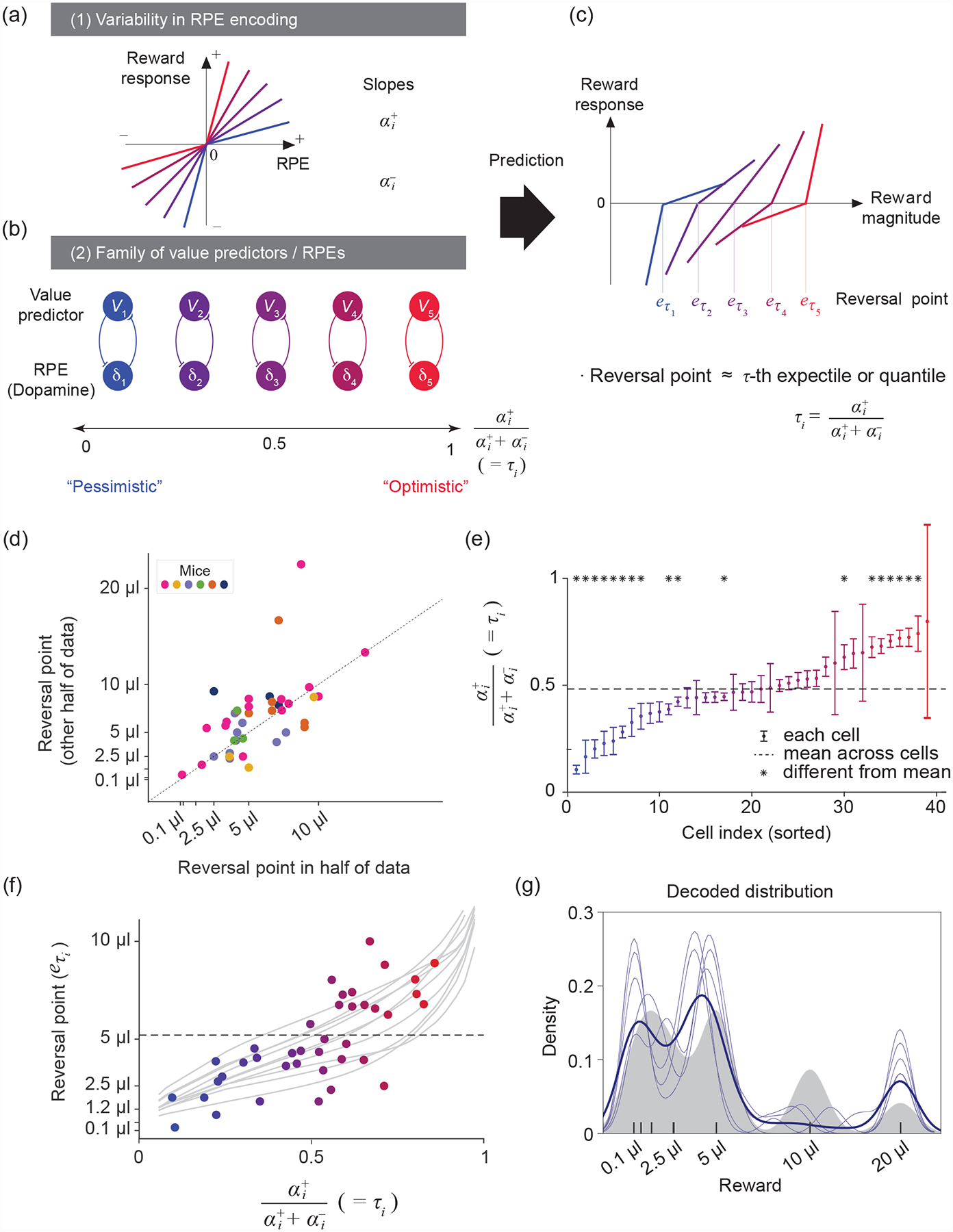
(a) Schematic of five different response functions (spiking activity of dopamine neurons) to positive and negative RPEs. In this model, the slope of the response function to positive and negative RPEs corresponds to the learning rates α+ and α−. Diversity in α+ and α− values results in different asymmetric scaling factors ().
(b) RPE channels (δi) with α+ < α− overweight negative prediction errors, resulting in pessimistic (blue) value predictors (Vi), while RPE channels with α+ > α− overweight positive prediction errors and result in optimistic (red) value predictors. This representation corresponds to the Rescorla-Wagner approach in which RPE and value pairs form separate channels, with no crosstalk between channels with different scaling factors. See Box 2 for the general update rule when this condition is not met.
(c) Given that different value predictors encode different reward magnitudes, the corresponding RPE channels will have diverse reversal points (reward magnitudes that elicit no RPE activity relative to baseline). The reversal points correspond to the values Vi of the τi-th expectiles of the reward distribution.
(d) Reversal points are consistent across two different halves of the data, suggesting that the diversity observed is reliable (P = 1.8 × 10−5, each point represents a cell). Modified after [8].
(e) Diversity in asymmetric scaling in dopamine neurons tiles the entire [0, 1] interval and is statistically reliable (one-way ANOVA; F(38,234) = 2.93, P = 4 × 10−7). Modified after [8].
(f) Significant correlation between reversal points and asymmetric scaling in dopamine neurons (each point is a cell, linear regression P = 8.1 × 10−5). Grey traces show variability over simulations of the distributional TD algorithm run to calculate reversal points in this task. Modified after [8].
(g) Decoding of the reward distribution from dopamine cell activity using an expectile code. The expectiles of the distribution, , were defined by the asymmetries and reversal points of dopamine neurons. Grey area represents the smoothed reward distribution, light blue traces represent several decoding runs, and the dark blue trace their mean. Modified after [8].
