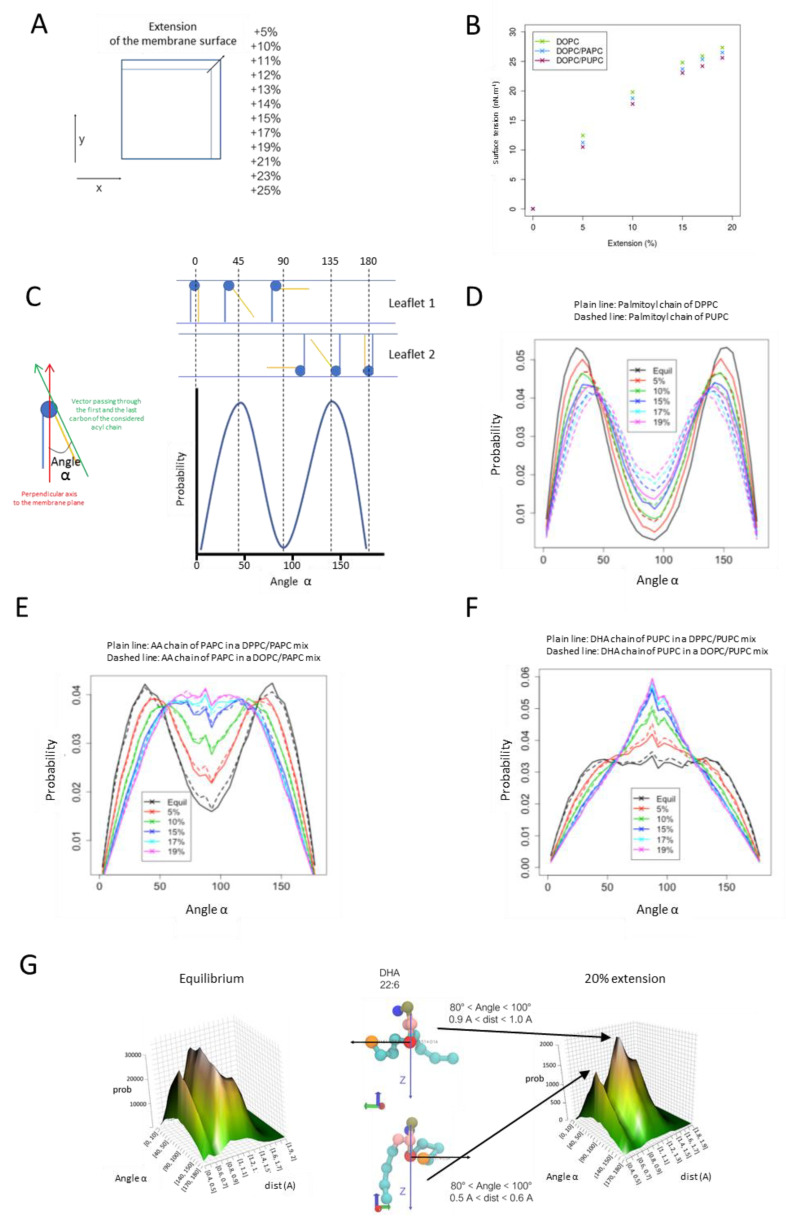
Figure 8.
Molecular dynamics simulations of simple membranes composed of PC bearing various fatty acid compositions in response to surface expansion. (A) To mimic surface expansion using molecular dynamics simulations, the values of the dimensions x/y of the system, corresponding to the membrane plane, were artificially increased. A first simulation is conducted at equilibrium, then the x/y is increased by 5% and blocked, so the membrane surface remains the same during the simulation (pressure is kept constant at 1 bar with the dimension z of the system). (B) Evolution of the surface tension as a function of surface expansion for membranes composed of PC species bearing various fatty acid compositions. DOPC: PC bearing two oleoyl chains; PAPC: AA at the sn-2 position of PC, in combination with palmitate; PUPC: DHA at the sn-2 position of PC, in combination with palmitate. (C) The angle α represents the angle between two vectors. The first vector is defined by the first and last beads of the acyl chain. The second vector is the perpendicular axis to the membrane plane. Angles close to 0° mean that the considered acyl chain of the PL is perpendicular to the membrane plane. By contrast, when the angle is close to 90°, the acyl chain is positioned in parallel to the membrane plane. Due to the two leaflets of a membrane, there are two symmetrical distributions. (D) Probabilities of the angle α to reach a given value for a palmitoyl chain as a function of surface expansion. Plain lines show the distributions of angles for a palmitoyl chain in DPPC (sn-1 position). Dashed lines show the distributions of angles for the palmitoyl chain of PUPC. DPPC: PC bearing two palmitoyl chains. (E) Probabilities of the angle α to reach a given value for an AA chain as a function of surface expansion. Plain and dashed lines show the distributions of angles for the AA chain from PAPC when mixed with either DPPC or DOPC, respectively. (F) Probabilities of the angle α to reach a given value for a DHA fatty acyl chain as a function of expansion surface. Plain lines show the distributions of angles for the DHA chain from PUPC lipids mixed with DPPC. Dashed lines show the distributions of angles for the DHA chain from PUPC lipids mixed with DOPC. (G) 3D probability graph of the DHA chain conformation in PUPC, either at equilibrium (left) or under 20% extension (right), as a function of the angle α and the distance between the first and last beads of the DHA chain (DOPC/PUPC mix). Representative conformations of the DHA chain of PUPC are displayed.