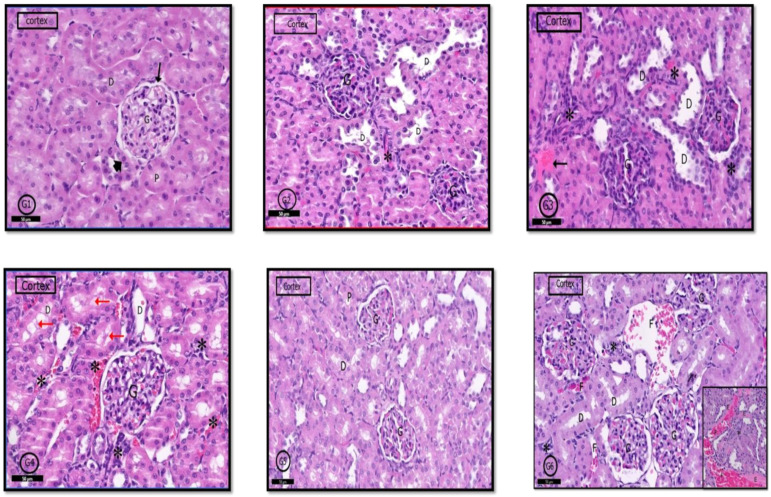
Figure 9.
Photomicrographs of the rat renal cortex of different groups: In control rats (G1), normal renal cortical parts like glomerulus (G) in Bowman’s capsule (↑). (PCT) proximal convoluted tubules (D,P) and (DCT) distal convoluted tubules (head arrow) were seen. (G2) (PILO rats) showed localized areas of degeneration in the form of hypertrophied glomerular capillary loops (G) with dark nuclei. DCT had wide lumen (D); in addition to infiltrated inflammatory cells (*). In (G3) (PILO+LPS rats) and (G4) (PILO+LPS+VPA rats), signs of cortical degeneration were evident in the form of sclerotic glomeruli (G), wide DCT (D), infiltrated inflammatory cells with hemorrhage (*) and areas of exudate (↑). (G5) (PILO+LPS+Celecoxib rats) showed nearly normal renal cortical architecture of renal corpuscle (G), PCTs (P), and DCTs (D). In general, (G6) (PILO+LPS+VPA+Celecoxib rats) showed similar architecture as control rats but in localized areas (see also inset), collapsed glomeruli (C), interstitial infiltration (*) and focal interstitial widening with hemorrhage (F) and pink exudate (E) were seen. Stain: H&E. Bars: 50 µm Inset ×400.