Figure 3.
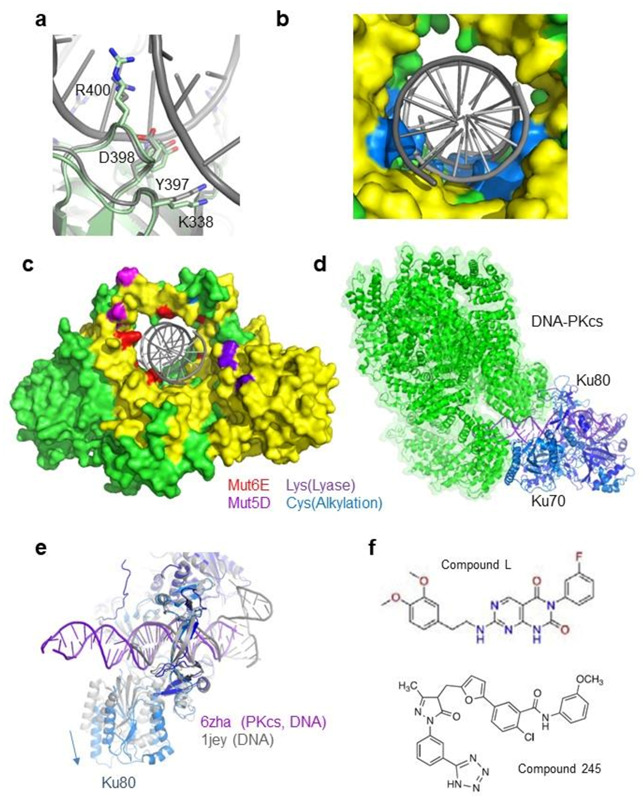
Complementarity between Ku inner ring and the DNA (a) Structure of an inner ring loop of Ku (Ku80 Tyr397-Arg400) that interacts with the minor groove of the DNA. The figure shows a superimposition of this loop in the Ku/DNA complex and Ku free structures. (b) Surface representation of the Ku inner ring. Ku residues in contact with the DNA grooves are colored in blue. Due to these contacts, the radius of the inner ring of Ku is smaller than the DNA radius. (c) Surface representation of Ku. Residues in red are the six Ku70 positions mutated in Glu to disrupt the Ku-DNA interaction [52] (positions Lys282, Lys287, Thr300, Lys331, Lys338, and Arg403). Residues in magenta are the five positions mutated in Asp in [53] to mimic potential phosphorylation sites on the ring (Thr305, Ser306, Thr307, Ser314, and Thr316). Residues in purple are positions of Ku70 lysines (Lys31, Lys160, and Lys164) proposed to be involved in the Ku dRP/Lyase activity [43] (Lys31 is not observe, the first amino acid of Ku70 visible in the crystal is Arg35). Residues in light blue are a Cys of Ku80 that is a potential site of alkylation [54]. (d) CryoEM structure of (Ku70/80)/DNA-PKcs/DNA complex (PDB 6zha) [11]. DNA-PKcs is represented in the green cartoon with a semi-transparent surface. Ku70 and Ku80 are, respectively, shown in light and dark blue, while DNA is shown in purple. (e) Superimposition of Ku from the Ku/DNA-PKcs/DNA complex and Ku from the Ku/DNA complex (PDB 1jey) [45]. The loops of Ku in contact with DNA superimpose well, indicating that Ku has the same inner ring conformation with or without DNA-PKcs. (f) Inhibitors of Ku-DNA interactions reported by [55] (compound L) and by [56] (compound 245).
