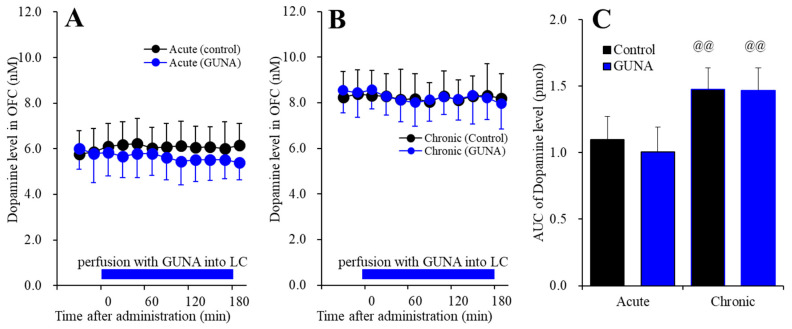
Figure 2.
Effects of acute local administration (perfusion with) 200 nM guanfacine into the LC on extracellular dopamine level in the OFC, after the systemically chronic administration of guanfacine (0 or 0.12 mg/kg/day for 14 days). Panel (A) indicates the effects of perfusion with 200 nM guanfacine into the LC after chronic administration of guanfacine (0 mg/kg/day) for 14 days (acute effects). Panel (B) indicates effects of 200 nM guanfacine after systemically chronic administration of guanfacine (0.12 mg/kg/day) for 14 days (chronic effects). Ordinates: mean±SD (n = 6) of extracellular dopamine level (nM), abscissa: time after administration of perfusion with guanfacine into the LC (min). Blue bars: perfusion of 200 nM guanfacine into LC. Panel (C) indicates the AUC20–180 min values of extracellular dopamine level during perfusion with guanfacine (from 20 to 180 min). Ordinates: mean ± SD (n = 6) of AUC20–180 min values of extracellular dopamine level (pmol). Black and blue columns indicate respective control and perfusion of guanfacine of AUC values of dopamine levels. When the effects of guanfacine were statistically significant compared using MANOVA, the data were analysed using Tukey’s post hoc test. @@ p < 0.01: compared with acute effects of guanfacine.