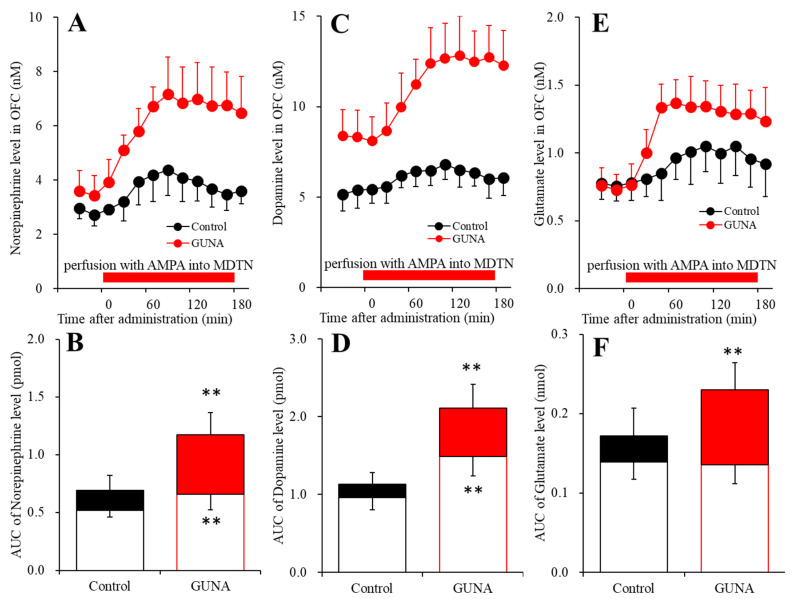
Figure 7.
Effects of acutely local administration (perfusion with) 100 μM α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) into the MDTN on extracellular levels of norepinephrine, dopamine and L-glutamate in the OFC, after the systemically chronic administration of guanfacine (0 or 0.12 mg/kg/day for 14 days). Panels (A,C,E) indicate the effects of perfusion with 100 μM AMPA into the MDTN after chronic administration of guanfacine (0 or 0.12 mg/kg/day) for 14 days on extracellular levels of norepinephrine, dopamine and L-glutamate in the OFC, respectively. Ordinates: mean±SD (n = 6) of extracellular levels of norepinephrine (nM), dopamine (nM) or L-glutamate (μM), abscissa: time after administration of perfusion with AMPA into the MDTN (min). Red bars: perfusion of 100 μM AMPA into the MDTN. Panels (B,D,F) indicate the AUC20–180 min values of extracellular levels of norepinephrine, dopamine and L-glutamate during perfusion with AMPA (from 20 to 180 min). Ordinates: mean ± SD (n = 6) of AUC20–180 min values of extracellular levels of norepinephrine (pmol), dopamine (pmol) and L-glutamate (nmol), respectively. Opened, black and red columns indicate AUC vales during pre-AMPA and AMPA-evoked releases control and chronic guanfacine administrations, respectively. When the effects of AMPA were statistically significant compared using MANOVA, the data were analysed using Tukey’s post hoc test. ** p < 0.01, compared with control.