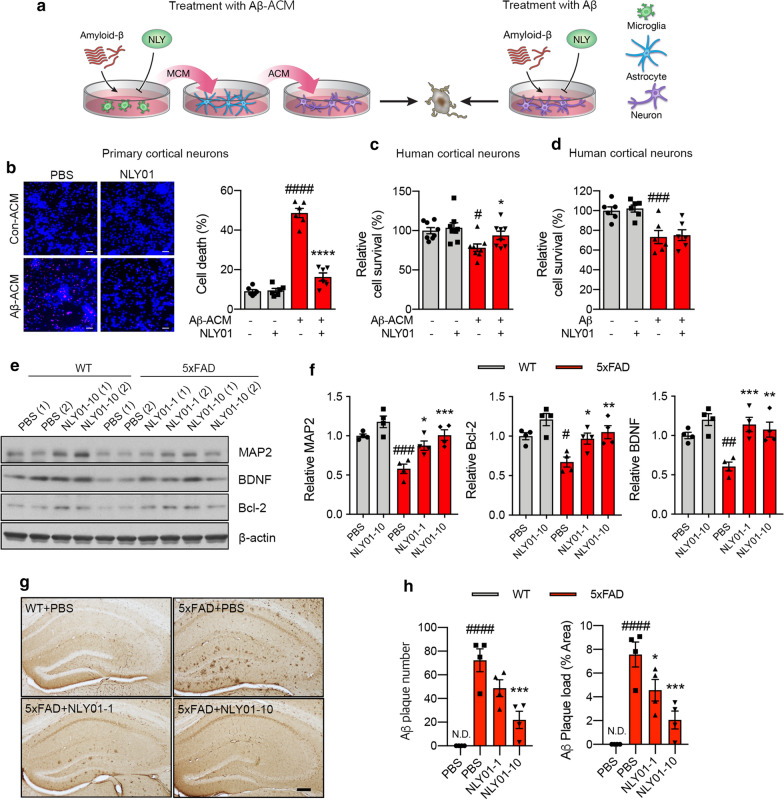
Fig.5.
Effects of NLY01 on neuronal cell death caused by Aβ1-42-induced DAA. a Schematic diagram showing treatment of neurons with Aβ1-42-astrocyte conditioned media (ACM) or directly with Aβ1-42. b Representative images showing the death of mouse primary cortical neurons (left; Propidium iodide stain in red indicates the dead cells) and quantification of cell death caused by Aβ1-42-ACM (15 μg/ml) with or without NLY01 (1 μM) (n = 6, 2 technical repeats from 3 biologically independent cell cultures). c Quantification of cell death caused by Aβ1-42-ACM (50 μg/mL) with or without NLY01 (1 μM) in human cortical neurons (n = 8, 2 technical repeats from 4 biologically independent cell cultures). d Quantification of cell death caused by Aβ1-42 treatment (5 μM) with or without NLY01 (1 μM) in human cortical neurons (n = 6). e Protein expression of MAP2, BDNF, Bcl-2, and β-actin in the hippocampus of WT and 5xFAD mice treated with PBS or NLY01. f MAP2, BDNF and Bcl-2 protein levels were normalized versus β-actin levels (n = 4 per group). g, h Aβ plaques were stained using 4G8 antibody in WT or 5xFAD mice with NLY01 treatment. g Representative images of immunostaining with 4G8 (scale bar, 200 μm) and h quantification of Aβ plaque number and Aβ load (n = 4 per group). Data are shown as the mean SEM. p values were determined by one-way ANOVA. #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001, ####p < 0.0001 versus Control or WT + PBS; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.001 versus Aβ-ACM, Aβ, or 5xFAD + PBS