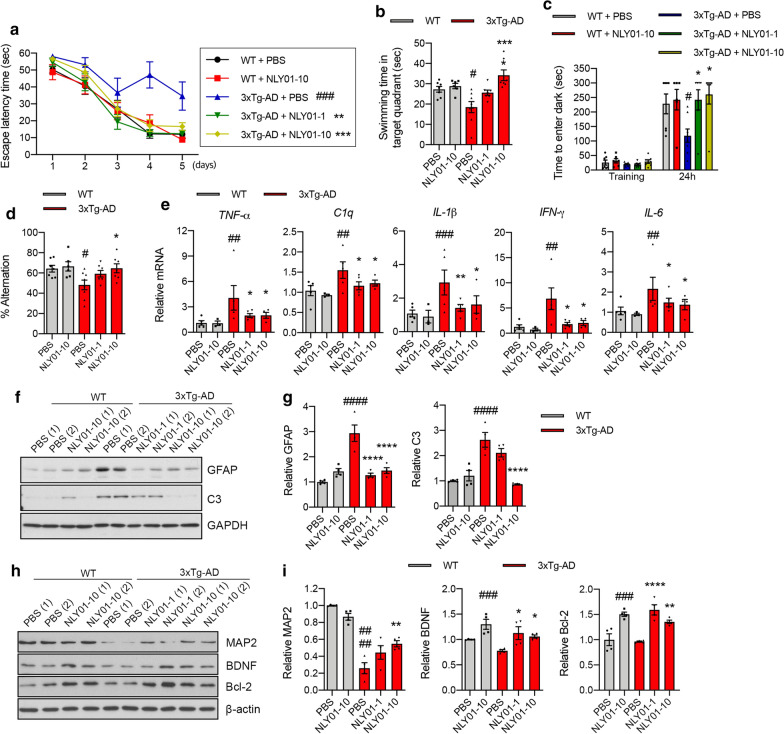
Fig. 6.
Effects of NLY01 on 3 × Tg-AD mice. 7-month-old 3 × Tg-AD mice treated with PBS or NLY01 (1 or 10 mg/kg) subcutaneously (s.c.) for 5 months (n = 6–8 per group). a Mice were trained and tested on the spatial memory version of the Morris water maze (MWM; indicated by solid lines at 60 s escape latency) (n = 6–8 per group). b Mice were given a memory probe with the platform removed at 24 h after the last training trial. 3 × Tg-AD mice treated with NLY01 exhibited dose-dependently increased time in the target quadrant (n = 6–8 per group). c Mice were placed in a light compartment and received a mild foot shock upon crossing over to the dark compartment. Mice were tested for retention of memory at 24 h after training (n = 6–8 per group). d Mice were tested on a spatial alternation task in a Y-maze (n = 6–8 per group). e The levels of TNF-α, C1q, IL-1β, IFN-γ, and IL-6 were analyzed by qPCR in the hippocampus of mice treated with PBS or NLY01 (n = 3–5 per group). f Protein expression of GFAP and C3 in the hippocampus from WT and 3xTg-AD mice treated with PBS or NLY01 using Western blot. g GFAP and C3 protein levels were normalized versus GAPDH levels (n = 4 per group). h Representative images of western blot with MAP2, BDNF, and Bcl-2. i Protein levels of (h) were normalized versus β-actin levels (n = 4 per group). Data are shown as the mean SEM. p values were determined by one-way ANOVA. #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001, ####p < 0.0001 versus WT + PBS; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001 versus 3xTg-AD + PBS