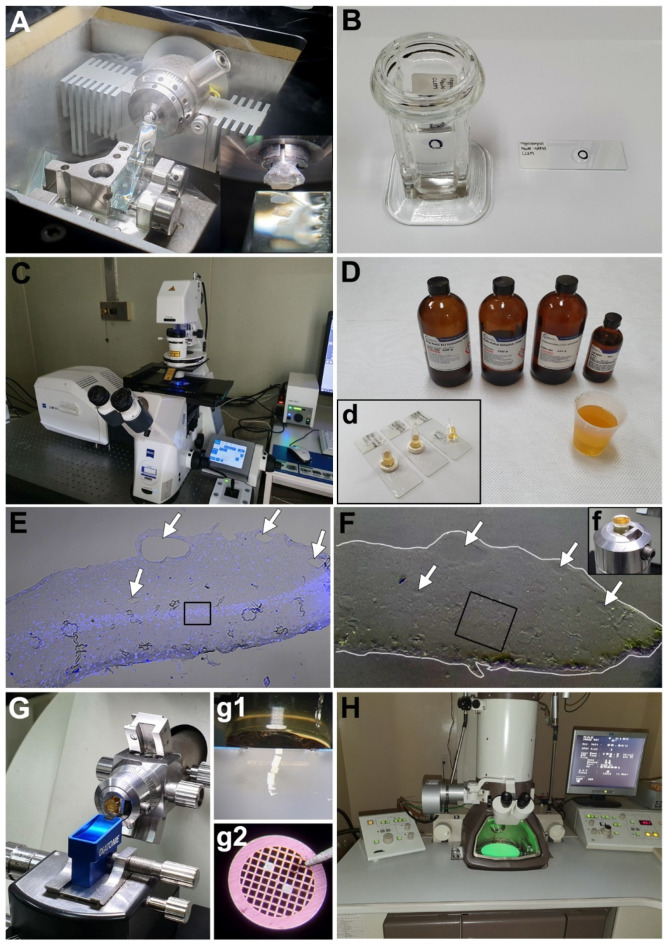
Figure 1.
Correlative light and electron microscopy (CLEM) procedures on thick cryo-sections from the hippocampus using FluoroNanogold. (A) Cryoprotected sample with 2.3 M sucrose is cut on a cryo-ultramicrotome with a glass knife at −90 °C (1-μm-thick sections). (B) The sections are mounted on a glass slide with the loop containing 2.3 M sucrose and incubated with the antibodies for immunocytochemistry. (C) Light-microscopic imaging is performed using a confocal microscope. (D,d) After fixation and silver enhancement, the sections are processed for routine transmission electron microscopy (TEM) preparation using a Poly/Bed 812 embedding media using microcentrifuge tubes. (E) Confocal image (E) with DAPI staining and differential interference contrast (DIC) settings shows clear contour of the tissue and vascular lumens (arrows). The boxed area in E indicates the region of interest. (F) Embedded block (f) was observed under a stereoscope for identification of morphological cues for alignment. The contour of the tissue block face is delineated in white line, and identical vascular structures seen in E are marked with arrows. The boxed area in F shows a fine trimming area. (G,g1) Polymerized block is trimmed and cut on an ultramicrotome with a diamond knife (80-nm-thick slices) without a semithin section. (g2) The section is mounted on a grid (100-mesh) and stained with uranyl acetate. (H) Region of interest imaged using light microscopy is observed using TEM.