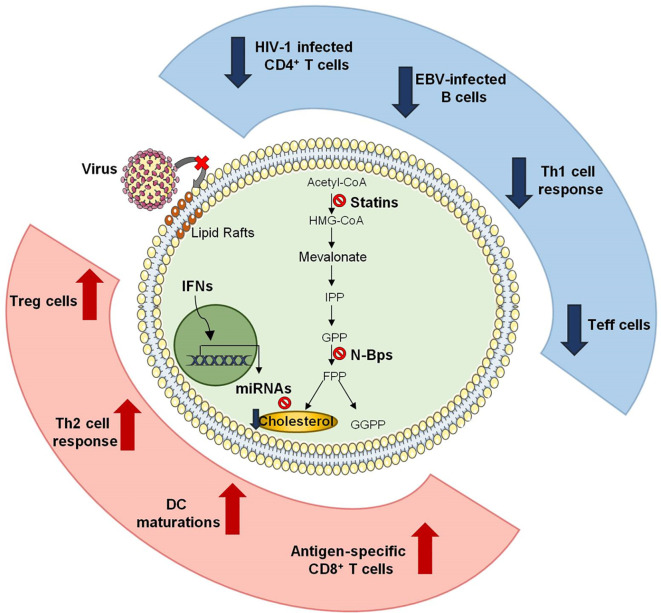
Fig. 2.
Effects of cholesterol-lowering drugs on anti-virus immune response. Schematic representation of how cholesterol-lowering drugs affect anti-viral immune responses. Depletion of cholesterol by statins alters lipid rafts in CD4+ T lymphocytes and avoids HIV-1 entry and its intracellular replication. Moreover, statin treatment results in the down-regulation of Th1 and in the induction anti-inflammatory Th2 response. During anti-viral immune responses statins also increase frequency and functions of Treg cells while inhibit effector functions of T lymphocytes. Cholesterol inhibition by bisphosphonate determines maturation of antigen presenting cells (APCs) which antigen-specific CD8+ T-cell responses. Finally, IFNs induce the production of specific miRNAs which modulate cholesterol levels in macrophages, thus improving their anti-viral activity.