Figure 1.
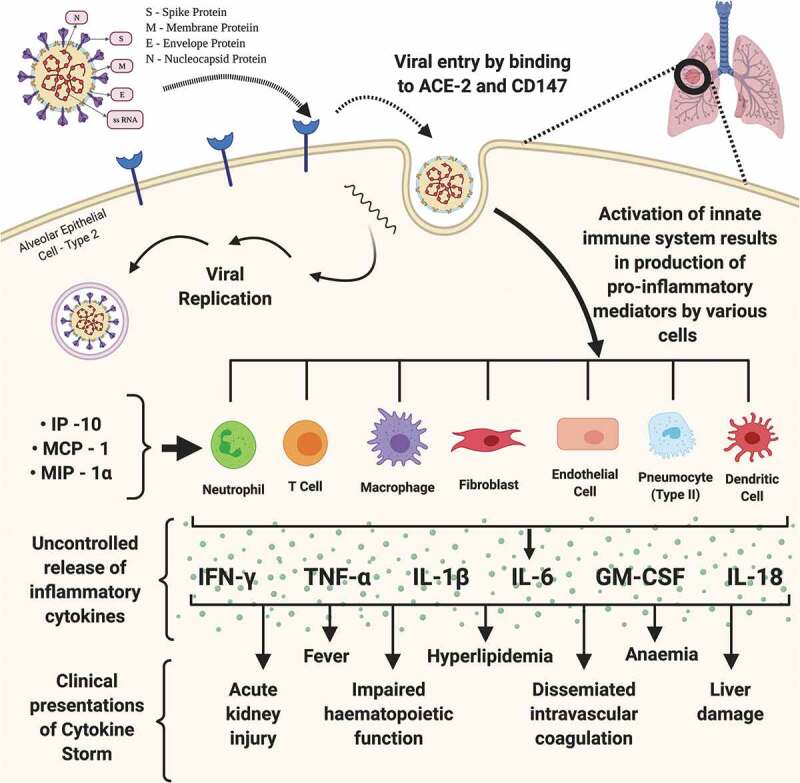
Pathogenesis of Cytokine Storm. The figure depicts the structure of SARS-CoV-2, its viral genome comprising of single stranded RNA and various viral proteins responsible for binding, entry and replication of the virus. Process of replication of SARS-CoV-2 begins with binding of viral S protein with the Angiotensin-Converting-Enzyme and CD147 receptors of the host leading to release of viral genome followed by its genomic and sub-genomic replication, and subsequent exocytosis of mature viruses. SARS-CoV-2 infection in the host lungs, upon its entry through the type 2 alveolar epithelial cells and interaction with the blood vessels at the pneumocyte – capillary interface, causes the activation of host innate immunity leading to the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which eventually results in an uncontrolled and exaggerated response, the cytokine storm. IL – interleukin; IP – interferon gamma-induced protein; MCP – monocyte chemoattractant protein; MIP – macrophage inflammatory protein; IFNγ – interferon gamma; TNFα – tumor necrosis factor alpha
