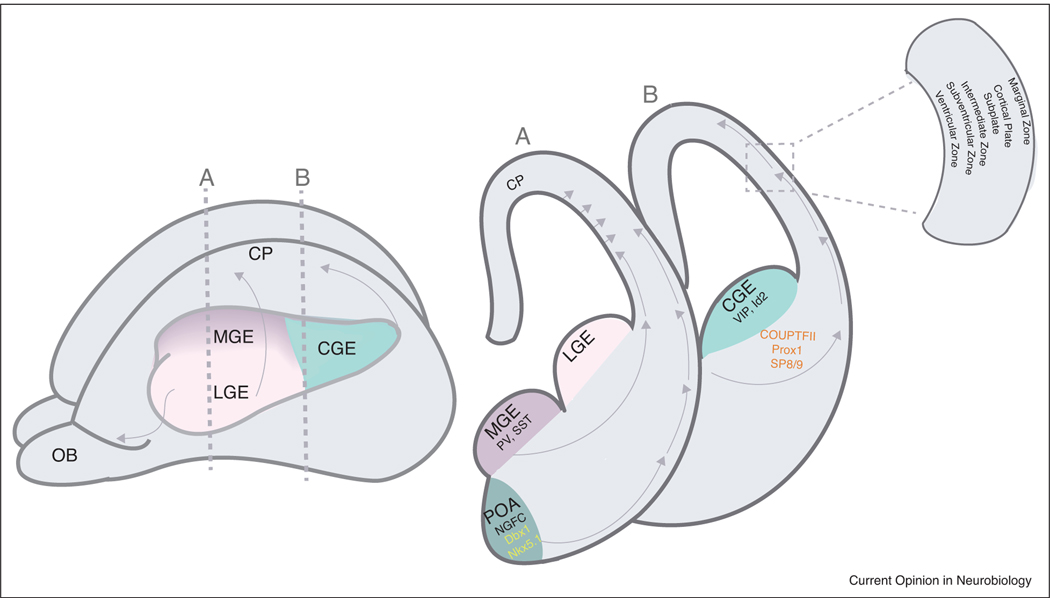
Figure 1.
Developmental origin of Layer 1 interneurons.
Left, schematic diagram of an embryonic mouse brain (~E14) highlighting the ganglionic eminences from which inhibitory interneurons are derived. Medial ganglionic eminence (MGE) gives rise to PV and SST interneurons, Lateral ganglionic eminence (LGE) gives rise to the interneurons of the olfactory bulb (OB); and Caudal ganglionic eminence (CGE) gives rise to the VIP and Id2 interneuron populations. Vertical dashed lines indicate the levels of the coronal sections in the right panel.
Right panel, coronal sections through the three eminences as well as the preoptic area (POA). Layer 1 interneurons are derived from the CGE and POA. Arrows indicate the routes of migration that the interneurons prefer to reach the cortical plate. Boxed inset highlights the structures surrounding the cortical plate present at this embryonic age.