Figure 1: TLVP treatment prevents systemic fluid retention.
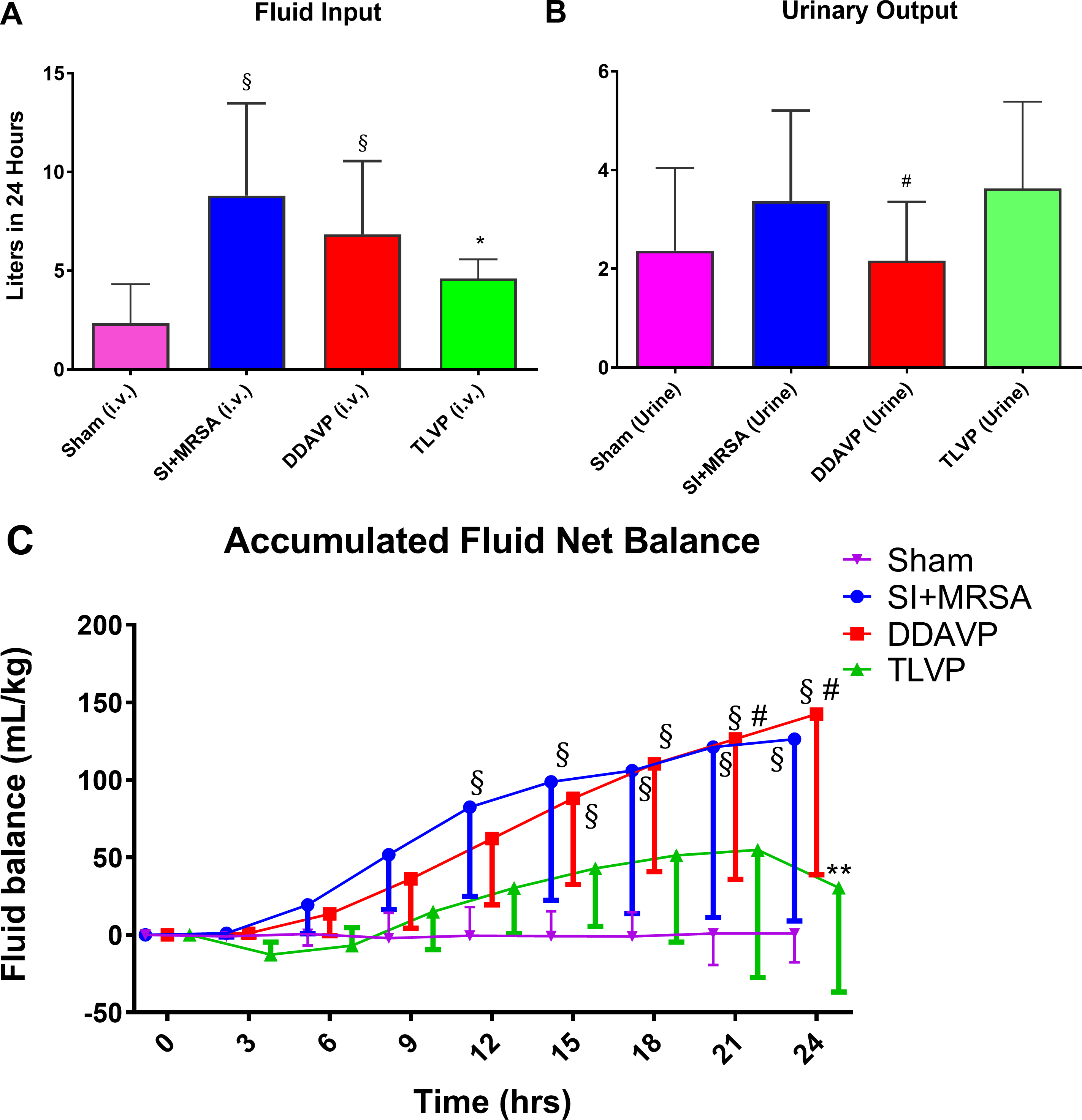
In vivo MRSA-induced sepsis model showing the different effects on fluid dynamics after treatment with tolvaptan (TLVP) or desmopressin (DDAVP) vs. no treatment (SI+MRSA) and no injured groups (Sham). (A) TLVP treatment significantly decreased the fluid requirement during sepsis (B) without having effects on urinary output. (C) As a result, SI+MRSA and DDAVP groups accumulated a large amount of fluids. TLVP treatment proved to be efficient in preventing this excessive amount of fluid retention during sepsis. The hematocrit was similar in all groups. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. *p <0.05 vs. SI+MRSA; #p <0.05 vs. TLVP; §p <0.05 vs. Sham.
