Figure 2: TLVP treatment attenuates pulmonary vascular damage and water retention.
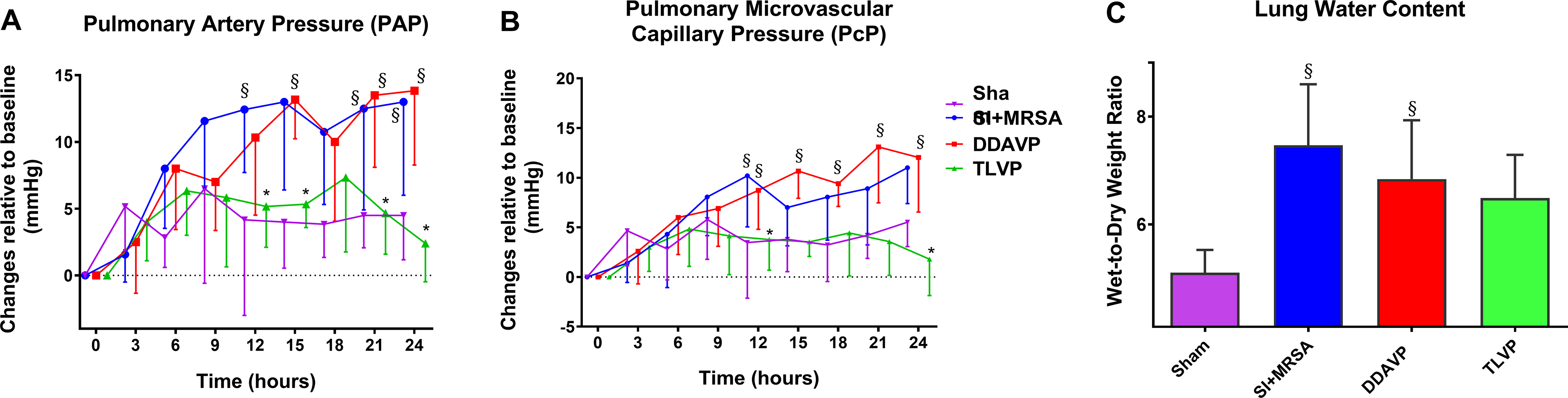
In vivo pulmonary intravascular pressure assessment (by invasive monitoring) and water content estimation (by W/D ratio). Following septic insult, the pulmonary microvasculature was affected demonstrating by (A) elevated in pulmonary resistance and (B) pulmonary microvascular capillary pressure, and (C) water retention in the lung tissue. TLVP treatment ameliorated the three parameters. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. *p <0.05 vs. SI+MRSA; §p <0.05 vs. Sham.
