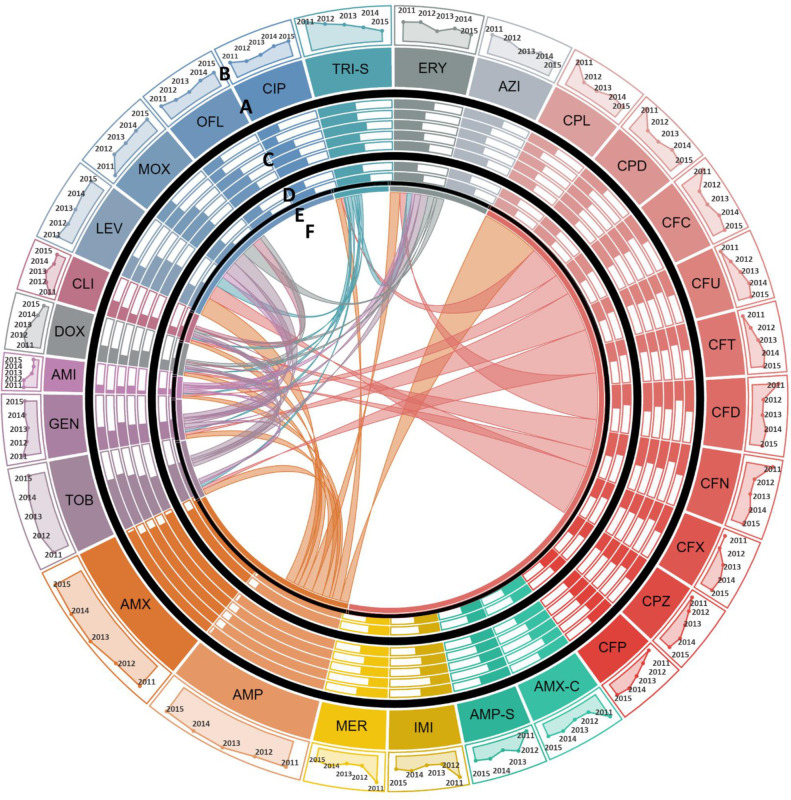
Fig 5. Antimicrobial resistance in Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus).
A: Each section of the diagram represents the resistance observed in S. aureus against the antibiotic. Size of each section is proportional to the proportion of S. aureus resistant to the antibiotic over the study period. Antibiotics of the same class are shown in similar colors. B: Line graphs show temporal trends of proportion of resistant S. aureus in a clockwise direction from 2011 to 2015. C: Bar charts show the comparison of susceptibility to resistant strains in patients of different age groups. Moving from out to inward, bars represent proportion of resistant S. aureus reported children in <5 years of age, young adults between 6 to 18 years, middle aged 19 to 45 years old, 45 to 65 years old patients, and elderly over 65 years of age, respectively. D: Gender-wise comparison to susceptibility to resistant S. aureus is shown in form bars. Outer circle and inner circle show proportion of resistant S. aureus isolated from women vs. men, respectively. E: For co-resistance analysis, antibiotics belonging to the same class with same susceptibility profile for all isolates of S. aureus were merged into a single variable. F: Proportion of S. aureus isolates resistant to one antimicrobial resistant to another antimicrobial are shown in the connections. The area covered by the connection on E is proportional to the level of co-resistance observed. Co-resistance proportions were scaled down to 1/10th of the actual overlap for visualization. Abbreviations: AMI: Amikacin, GEN: Gentamicin, TOB: Tobramycin, AMP: Ampicillin, AMX: Amoxicillin, IMI: Imipenem, MER: Meropenem, CPL: Cephalexin, CPD: Cephradine, CFC: Cefaclor, CFU: Cefuroxime, CFT: Cefotaxime, CFD: Ceftazidime, CFN: Ceftriaxone, CFX: Cefixime, CPZ: Cefoperazone, CFP: Cefepime, AMX-C: Amoxicillin-Clavulanic acid, AMP-S: Ampicillin-Sulbactam, CIP: Ciprofloxacin, LEV: Levofloxacin, OFL: Ofloxacin, MOX: Moxifloxacin, CLI: Clindamycin, AZI: Azithromycin, ERY: Erythromycin, TRI-S: Trime-Sulphamethoxazole, and DOX: Doxycycline.