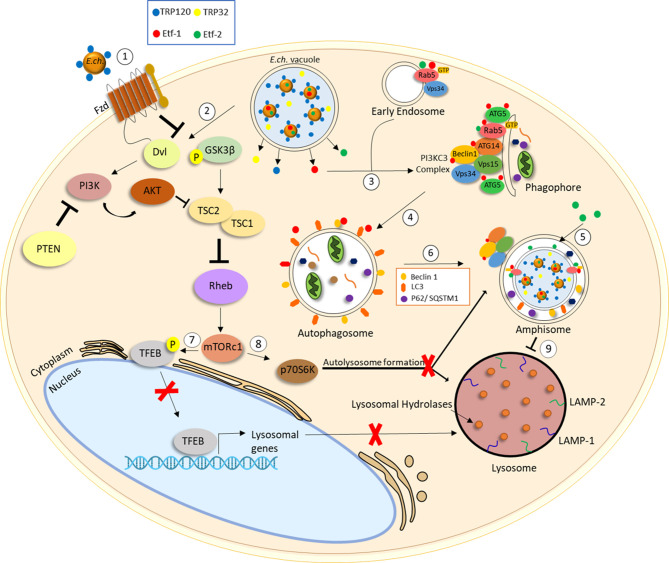
Figure 2.
E. chaffeensis interplay with the autophagic pathway. (1) E. chaffeensis dense-cored cells express effectors important for Wnt signaling including T1SS effectors TRP120 and TRP32. E. chaffeensis stimulates phagocytosis for entry through interaction between TRP120 and the Fzd receptor/co-receptor complex. (2) E. chaffeensis-mediated Wnt-PI3K/Akt signaling stimulates increased levels of phospho-GSK3-β reducing TSC2 and increasing Rheb activity leading to mTOR activation. (3) E. chaffeensis T4SS effector Etf-1 is secreted into the host cell cytoplasm and interacts with Beclin1, PI3CK complex and Rab5-GTP to stimulate phagophore formation. (4) ATG5 and LC3 engage to induce autophagosome formation in a class III PtdIns3K-dependent manner. (5) E. chaffeensis T4SS effector Etf-2 localizes to E. chaffeensis vacuole membrane and binds to RAB5-GTP to delay endosome maturation. (6) Autophagosomes displaying Beclin1, LC3II and p62/SQSTM1 fuse with E. chaffeensis inclusions to form amphisomes. (7) mTOR activation leads to TFEB phosphorylation and inhibition of TFEB nuclear translocation. Inhibition of TFEB nuclear translocation prevents transcription of genes involved in lysosomal biogenesis and (8) increased phospho-p70 S6 kinase activity inhibits autolysosome formation.