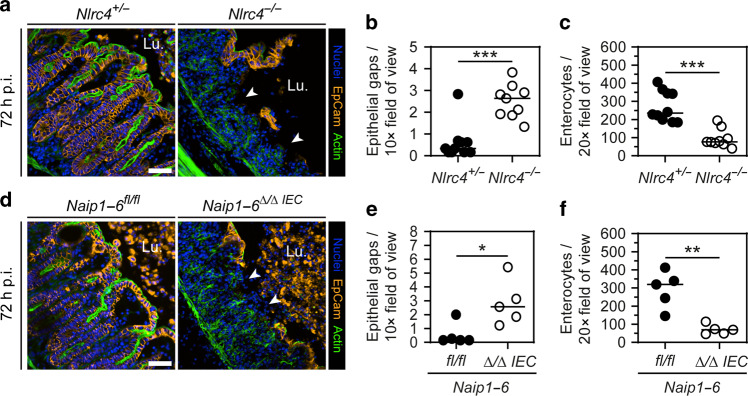
Fig. 1. Epithelial integrity loss at 72 h of S.Tm infection in NAIP/NLRC4-deficient mice.
a–c NLRC4-deficient mice lose epithelial integrity at late-stage S.Tm infection. a Representative micrograph of cecal tissue from (streptomycin pretreated) orally S.Tm-infected Nlrc4+/− control mice and Nlrc4−/− littermates at 72 h p.i. White arrowheads indicate epithelial gaps. Lu. lumen. Scale bar: 50 µm. b Microscopy-based quantification of epithelial gaps per 10× field of view. Detection limit at 0.17. c Microscopy-based quantification of enterocyte numbers within the epithelium per 20× field of view. d–f Deletion of epithelial NAIP1–6 is sufficient to cause severe epithelial integrity loss. d Representative micrograph of cecal tissue from S.Tm-infected Naip1–6fl/fl control mice and Naip1–6Δ/Δ IEC littermates at 72 h p.i. White arrowheads indicate epithelial gaps. Lu. lumen. Scale bar: 50 µm. e Microscopy-based quantification of epithelial gaps per 10× field of view. Detection limit at 0.15. f Microscopy-based quantification of enterocyte numbers within the epithelium per 20× field of view. b, c, e, f Each data point represents one mouse. Line at median. Five to ten mice per group from ≥2 independent experiments for each comparison. Mann–Whitney U test (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001).