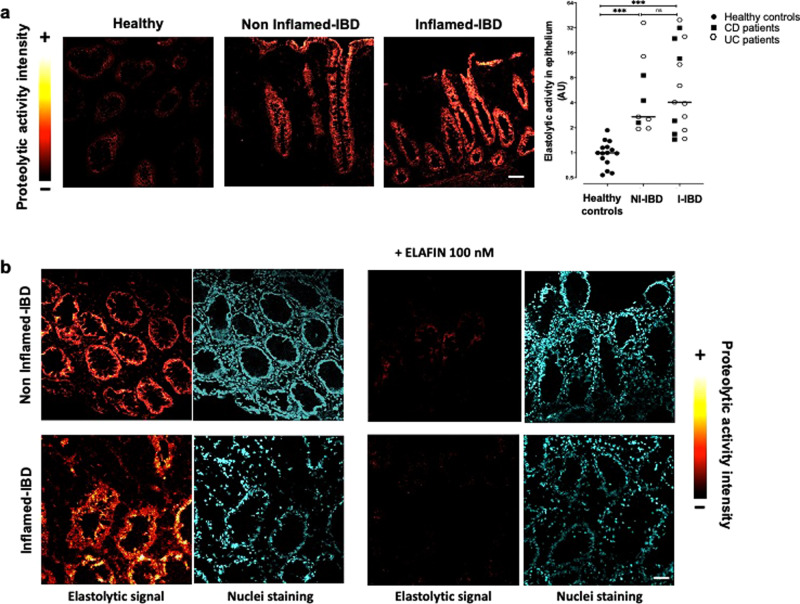
Fig. 1. Elastolytic activity is increased in epithelial cells from IBD colonic biopsies.
a In situ zymography of elastolytic activity in colonic mucosal biopsies from control groups (healthy) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) patients taken in non-inflamed and inflamed areas. Images colouring correspond to the intensity of fluorescence released after the proteolytic cleavage of elastine substrate according to the reported scale. Representative images of healthy controls tissue section (n = 15), non-inflammatory (NI-IBD) (n = 9), and inflammatory (I-IBD) areas from IBD patients (n = 15). Medians are represented. ***p < 0.001 compared to healthy patients using two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test. Scale bar = 20 μm. b In situ zymography of elastolytic activity in colonic mucosal biopsies in presence or not of 100 nM of ELAFIN, an elastase inhibitor, added exogenously to the tissue slices. These pictures are representative images generated in five patients suffering from CD and UC and healthy control patients. DAPI staining showing nuclei is also represented for each section. Scale bar = 50 μm.