Fig. 1.
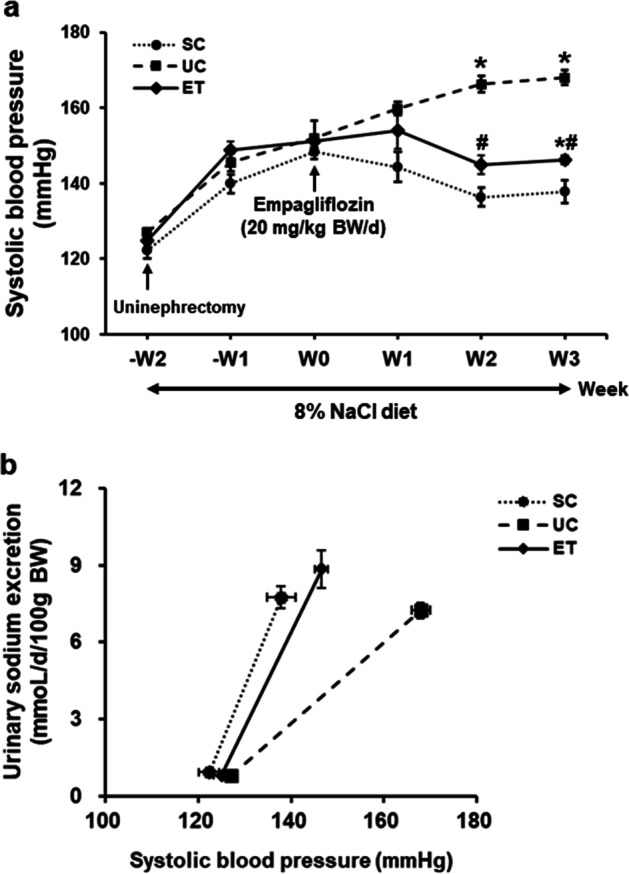
Comparisons of systolic blood pressure with empagliflozin treatment. All male Sprague-Dawley rats were fed a rodent diet with 8% NaCl for 5 weeks. To induce salt-sensitive hypertension, uninephrectomy was performed at the beginning. After 2 weeks of uninephrectomy, empagliflozin was orally administered for 3 weeks. Systolic blood pressure was measured weekly by a tail-cuff (a). Urinary sodium excretion and systolic blood pressure were compared in the context of the pressure–natriuresis relationship between the UC and ET rats (b). SCs, sham controls (n = 4); UCs, uninephrectomized controls (n = 4); ETs, empagliflozin-treated rats (n = 5). *P < 0.05 vs. SCs; #P < 0.05 vs. UCs by the Mann–Whitney U test
