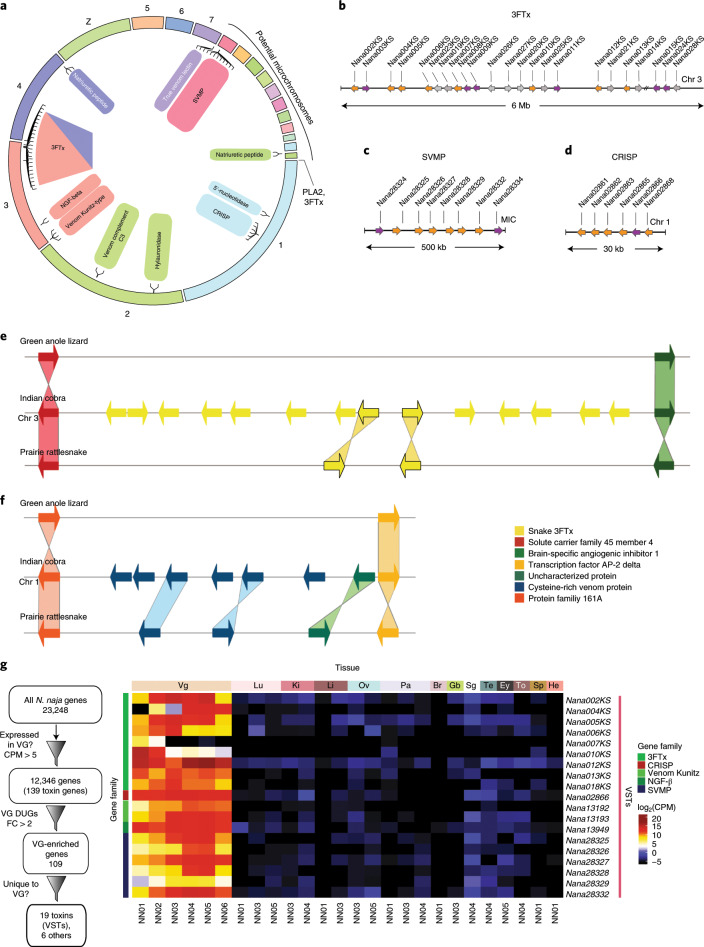
Fig. 4. The N. naja venom gene repertoire.
a, Genomic organization of N. naja toxin gene families. b–d, Arrayed venom gene organization of three major toxin gene families: 3FTx (b), SVMP (c) and CRISP (d). Genes that show venom-gland-specific expression are colored orange, and those with expression not restricted to venom glands are shown in magenta. Pseudogenes with no evidence for expression are shown in gray. e,f, Comparison showing the ancestral 3FTx (e) and CRISP (f) genes in lizard, and duplicated copies in the Indian cobra and prairie rattlesnake genomes. Orthologous gene pairs are indicated by shaded regions across the corresponding genomic regions. g, Schematic of filtering used to identify the 19 VSTs, and a heatmap showing the corresponding log2(CPM) values. NN01 and NN02 correspond to N. naja specimens obtained from Kerala, India. NN03, NN04, NN05 and NN06 correspond to N. naja specimens obtained from the Kentucky Reptile Zoo. FC, fold change; Chr, chomosome. Anatomical abbreviations as in Fig. 3.