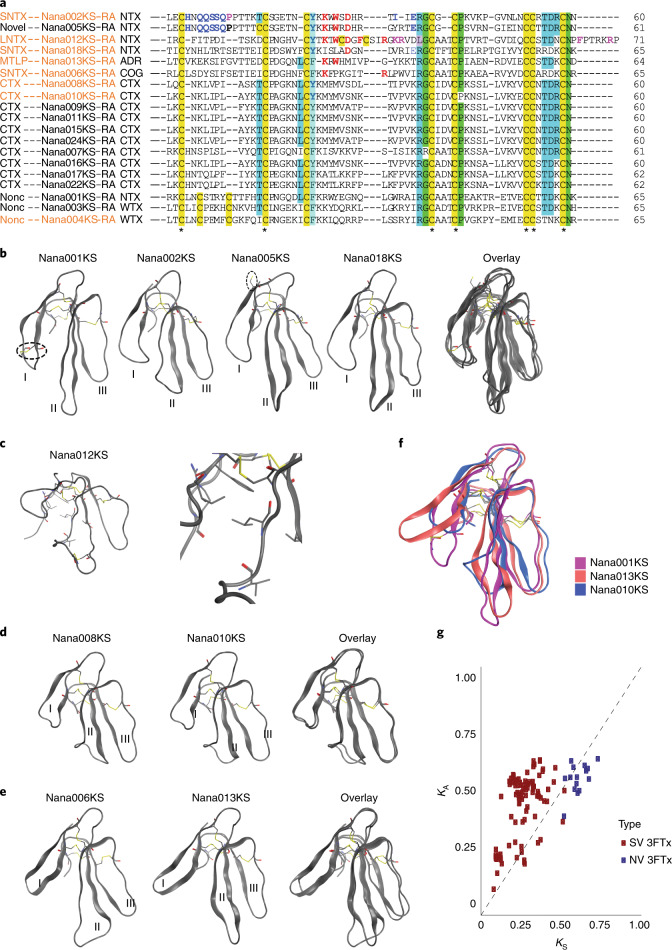
Fig. 5. Characterization of N. naja 3FTx gene family.
a, Multiple sequence alignment of the 19 3FTx proteins identified in the Indian cobra genome. Protein names in orange in the alignment indicate VSTs identified using RNA-seq. Conserved Cys residues are highlighted yellow in the alignment. b–e, Ribbon representations of representative 3FTxs from four different structural classes. Disulfide bonds are shown as sticks. The hydrophobic packing of Leu39 and surrounding residues is shown in c. Dashed circles highlight the additional disulfide bonds in Nana001KS, Nana012KS and the unpaired Cys in Nana005KS. f, Superimposition of ribbon models of Nana001KS, Nana003KS and Nana010KS highlighting the differences in loop length and conformation between the distinct classes of 3FTx found in the Indian cobra genome. g, Analysis of evolutionary rates on 3FTx venom genes and their non-venom paralogs. KA and KS values were calculated according to the Nei–Gojobori method. KA and KS with values <1 were not included in further analysis. SNTX, short neurotoxin; LNTX, long neurotoxin; MTLP, muscarinic toxin-like; CTX, cardiotoxin or cytotoxin; Nonc, non-conventional toxin; WTX, weak neurotoxin. SV, snake venom; NV, non-venom.