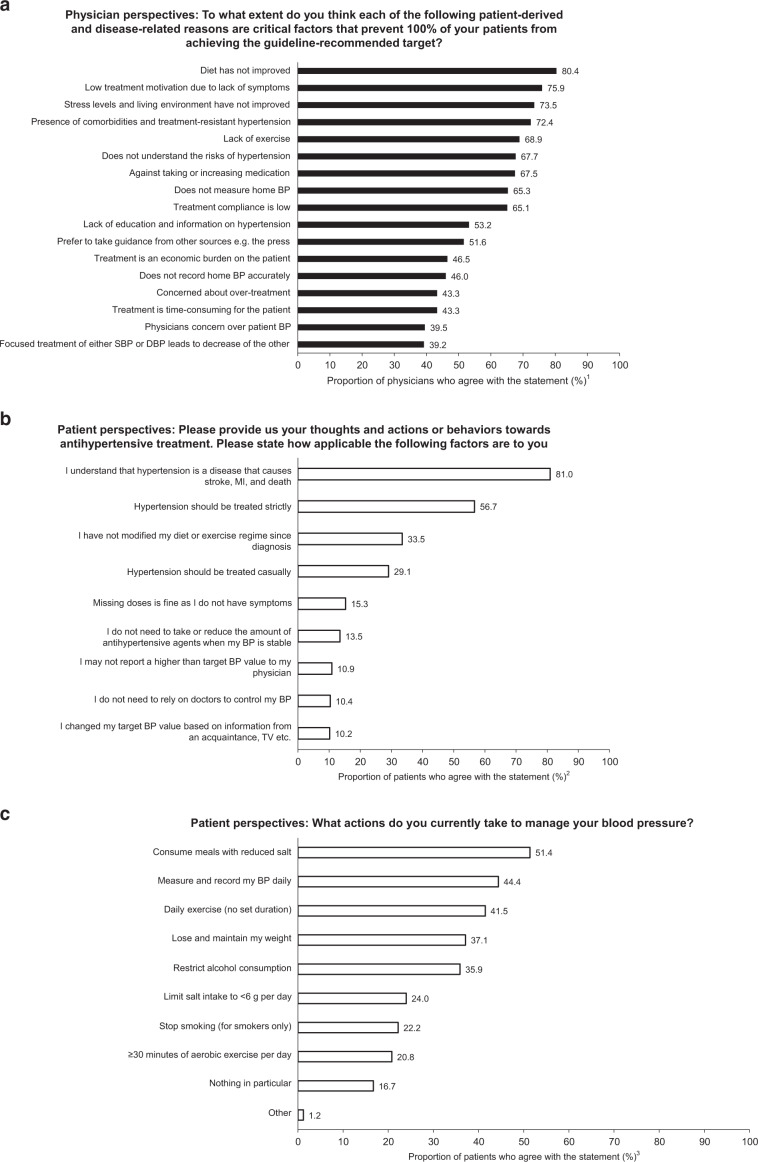
Fig. 1.
Patient and physician beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors toward hypertension management. a Physician-reported factors contributing to patients’ failure to achieve blood pressure targets; b patients’ attitudes toward hypertension treatment and their associated behaviors; and c patient-reported lifestyle changes for blood pressure management. BP blood pressure, DBP diastolic blood pressure, MI myocardial infarction, SBP systolic blood pressure, TV television. 1Percentage of physicians responding in each category with the answers “very significant” or “significant.” Based on physician question Q21 (Supplementary Document 2; to what extent do you think each of the following patient-derived and disease-related reasons are critical factors that prevent 100% of your patients from achieving the guideline-recommended target? Please select the most appropriate response for each of the following factors [scale ranging from “very significant” to “not significant at all”]). 2Percentage of patients who answered “very applicable” and “somewhat applicable” for each item. Based on the patient screening question SC13 (Supplementary Document 3; Please provide us your thoughts and actions or behaviors regarding antihypertensive treatment. Please select the most appropriate response for each of the following [scale ranging from “very applicable” to “not at all applicable”]). 3Percentage of patients who answered “yes” for each item. Based on patient question Q4 (Supplementary Document 4; what actions do you currently take to manage your blood pressure? Please select all the factors that apply to you from the following options)