Figure 4. Urine supersaturation of CaP and CaOx.
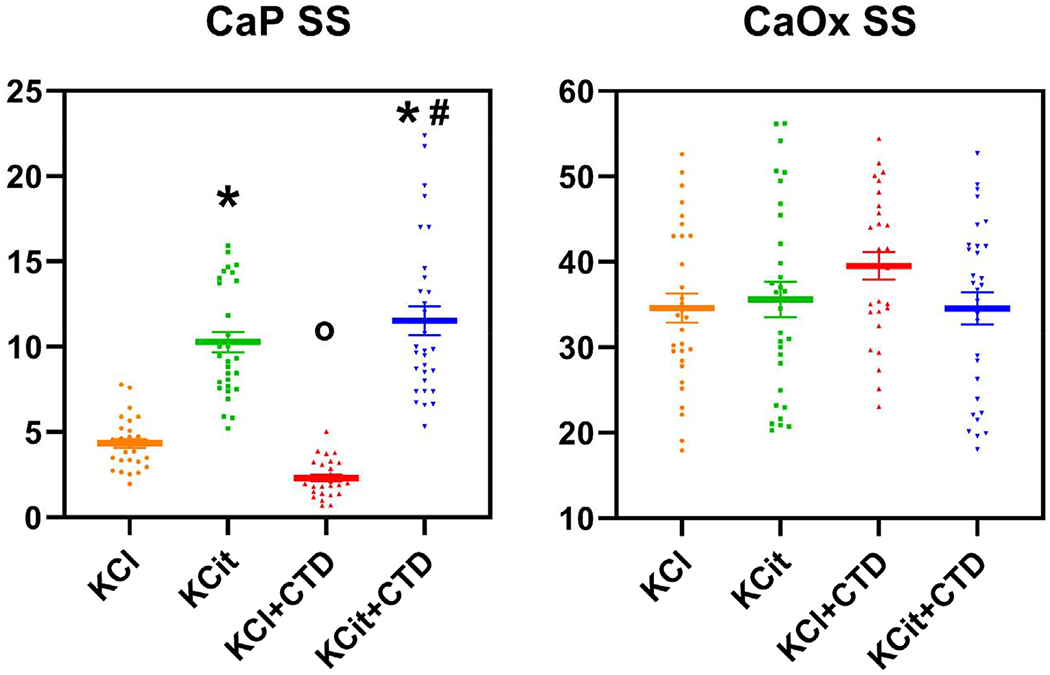
Rat diets were all supplemented with hydroxyproline and with either KCl (4 mmol/d) as a control, potassium citrate (KCit, 4 mmol/d), chlorthalidone (CTD, 4-5mg/kg/d) + KCl or KCit+CTD. Twenty-four-hour urine collections were done at 6, 12 and 18 wks for analysis of solute levels as described in Methods. These values were used to calculate relative supersaturation and an overall mean of all three collections was calculated. Values for relative supersaturation are unitless. Results are mean±SE for 10 rats/group. *p<0.05 vs KCl, op<0.05 vs KCit alone, #p<0.05 vs CTD alone.
