Figure 6. Changes in bone parameters after 18 weeks.
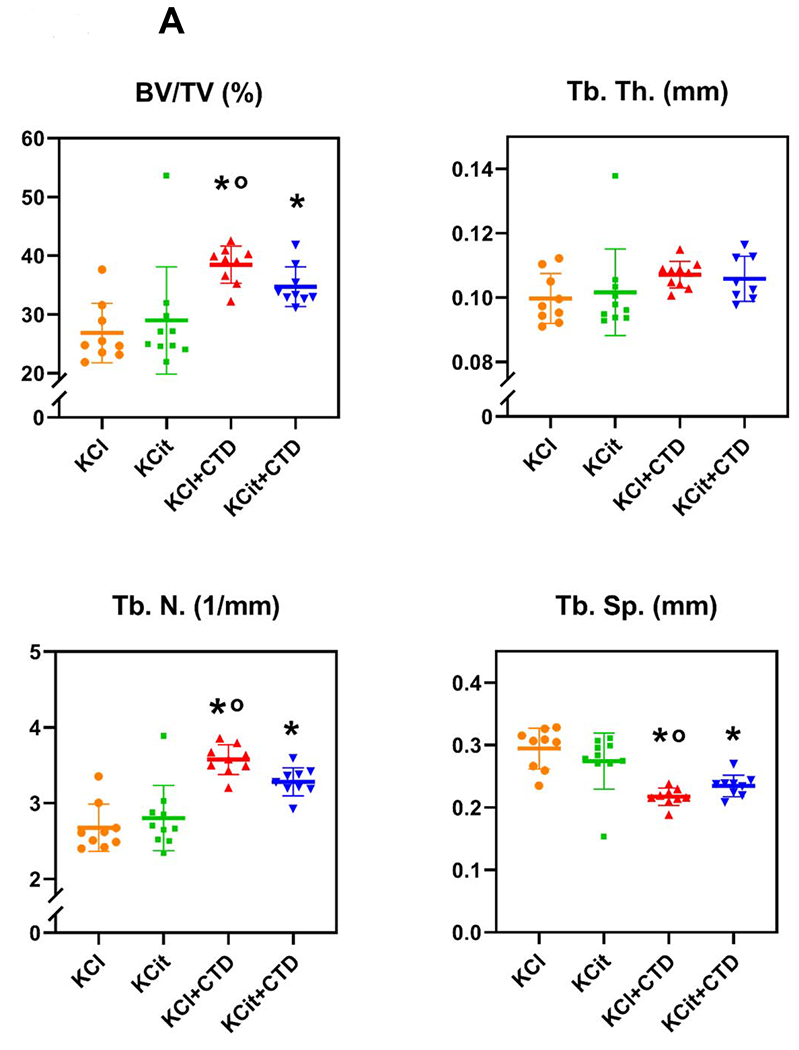
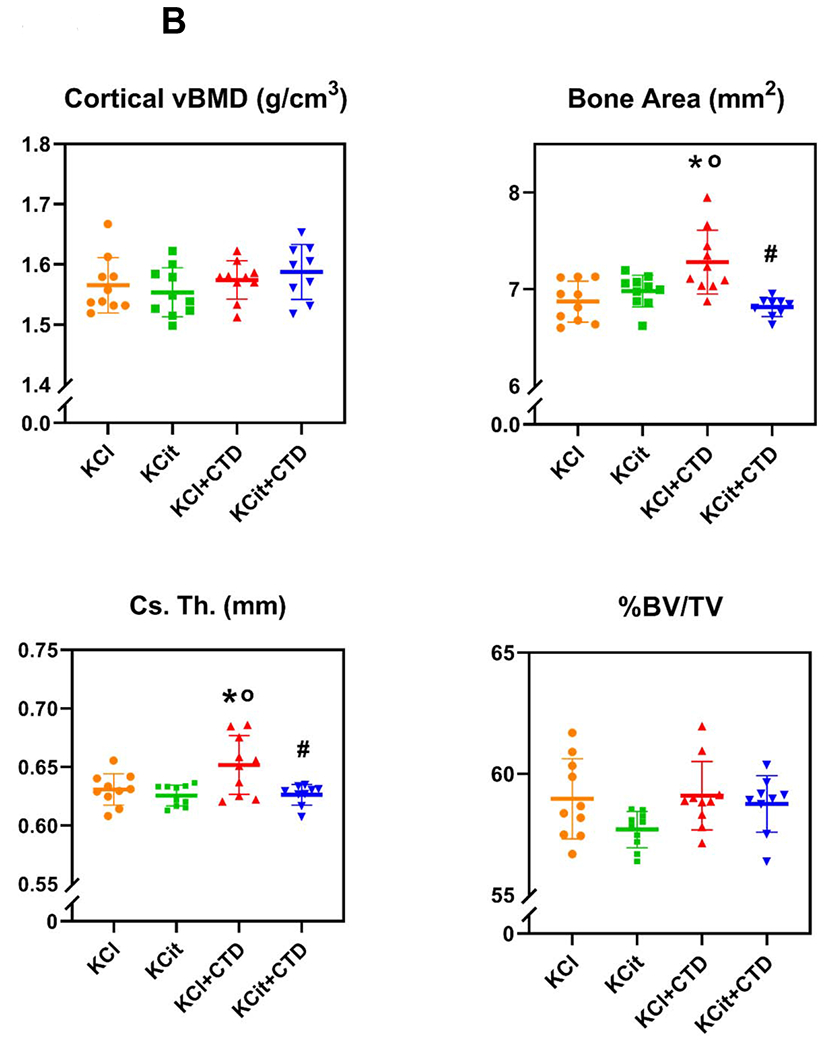
Rat diets were all supplemented with hydroxyproline and with either KCl (4 mmol/d) as a control, potassium citrate (KCit, 4 mmol/d), chlorthalidone (CTD, 4-5mg/kg/d) + KCl or KCit+CTD. At the conclusion of the 18 wk study, bones were collected from all rats and analyzed as described in Methods. A) Percent bone volume (BV/TV), trabecular thickness (Tb.Th.), trabecular number (Tb.N.) and trabecular separation (Tr. Sp.) of L6 vertebrae are presented. B) Cortical volumetric bone mineral density (vBMD), bone area (B.Ar.), cortical thickness (Cs.Th), and % bone volume/total volume (%BV/TV) of femoral cortical bone are presented. Results are mean±SD for n=10 bones/group. p<0.05 vs KCl, op<0.05 vs KCit alone. There were no significant differences comparing KCl+CTD to KCit+CTD.
