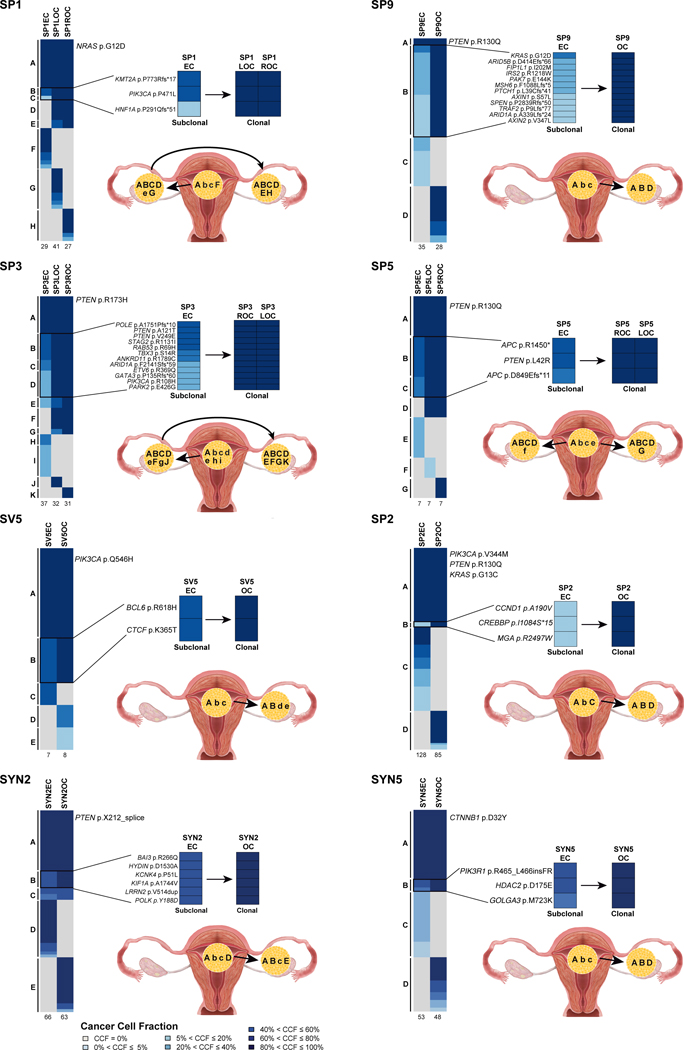
Figure 4: Clonal composition analysis and directionality of progression of sporadic synchronous endometrioid endometrial and endometrioid ovarian cancers.
Re-analysis of sporadic synchronous endometrial (ECs) and ovarian cancers (OCs) [12] subjected to whole-exome sequencing (SYN2, SYN5) or targeted MSK-IMPACT sequencing (SP1, SP2, SP3, SP9, SV5, SP5). Cases for which chronology of development could be inferred based on clonal composition analysis are shown. For each case, cancer cell fractions of somatic mutations identified in the EC and synchronous OC are depicted, color coded according to the legend, with detailed view of subclonal mutations in the EC that became clonal in the OC on the right. Total number of somatic mutations identified in a given EC and OC are below the heatmaps. Directionality of progression from the EC to the OC based on the clonality of mutations (capital letters, clonal; lower case letters, subclonal) are shown in the bottom right. CCF, cancer cell fraction; EC, endometrial carcinoma; OC, ovarian carcinoma.