Figure 4: Genotype and phenotype analysis of knock-in Myo9AR701X mice at 2 weeks of age.
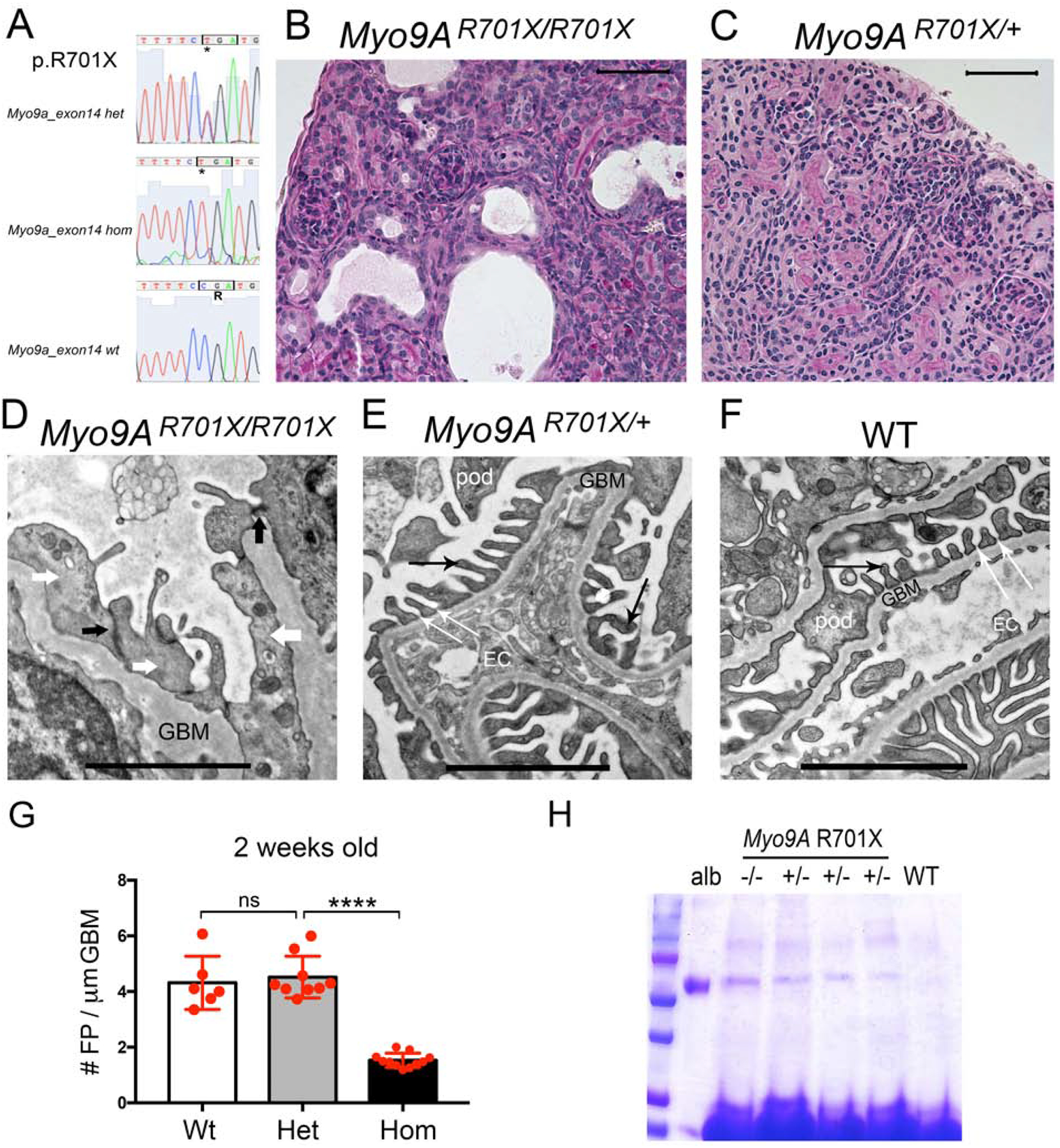
A) Sanger sequencing traces and deduced amino acid sequence from exon 14 are shown from mutant mice: heterozygous Myo9AR701X/+ (top), homozygous Myo9AR701X/R701X (middle) and wild type littermate (bottom); C>T mutation substitutes CGA encoding Arg (R) by TGA, a stop codon that predicts termination of translation at amino acid 701. B) Representative PAS stain from 2-week-old homozygous Myo9AR701X/R701X mutant kidney shows abnormal glomeruli, tubular dilatation and protein casts. C) Representative PAS stain from 2-week-old heterozygous Myo9AR701X/+ kidney shows normal histology. D) Representative TEM from 2-week-old Myo9AR701X/R701X glomerulus shows massive foot process effacement (white arrows), absence of slit-diaphragms, replaced by adherens junctions (black arrows) and thickened, irregular GBM. E) Representative TEM from 2-week-old heterozygous Myo9AR701X/+ glomerulus shows normal foot processes (black thin arrows), and normal slit-diaphragms (white thin arrows). F) TEM from 2-week-old wild type littermate (WT) shows normal glomerular filtration barrier: thin foot processes linked by slit-diaphragms, fenestrated endothelial cells and thin GBM. G) Quantitation of foot process effacement at 2 weeks of age: homozygous Myo9AR701X/R701X kidneys show less than half foot processes/μm GBM than willd type or heterozygous Myo9AR701X/+ littermates, indicating severe FPE , P<0.0001 (ANOVA). H) Coomassie blue stain of SDS-PAGE resolved urine samples shows albuminuria in both Myo9AR701X/R701X (−/−) and Myo9AR701X/+ (+/−), while WT urine is albumin free. BSA (10μg) serves as MW control. Scale bars: A and B= 20μm; C, D and E= 1μm.
