Figure 1. Male and female rats both acquire context fear memories.
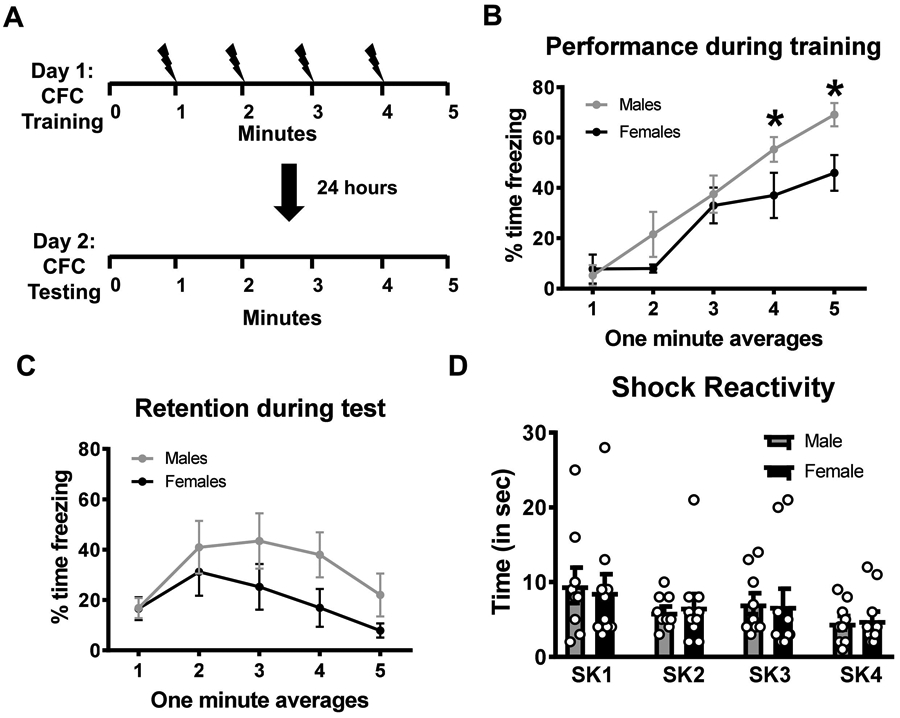
Young adult male and female rats (n = 10 per sex) were trained on a contextual fear conditioning paradigm and tested the following day for the retention to the training context. (A) Schematic of the training protocol in which 4 shocks were delivered over a 5 minute session. (B) Males showed higher freezing behavior than females during the training session, however, (C) both groups performed similar during the memory retention test. (D) Shock reactivity analysis did not reveal any differences between males and females in response to the shock stimulus during the training session. * p < 0.05 from Females.
