Figure 5. CRISPR-dCas9-KRAB-MECP2-mediated reductions in baseline protein degradation in the amygdala impairs fear memory in females.
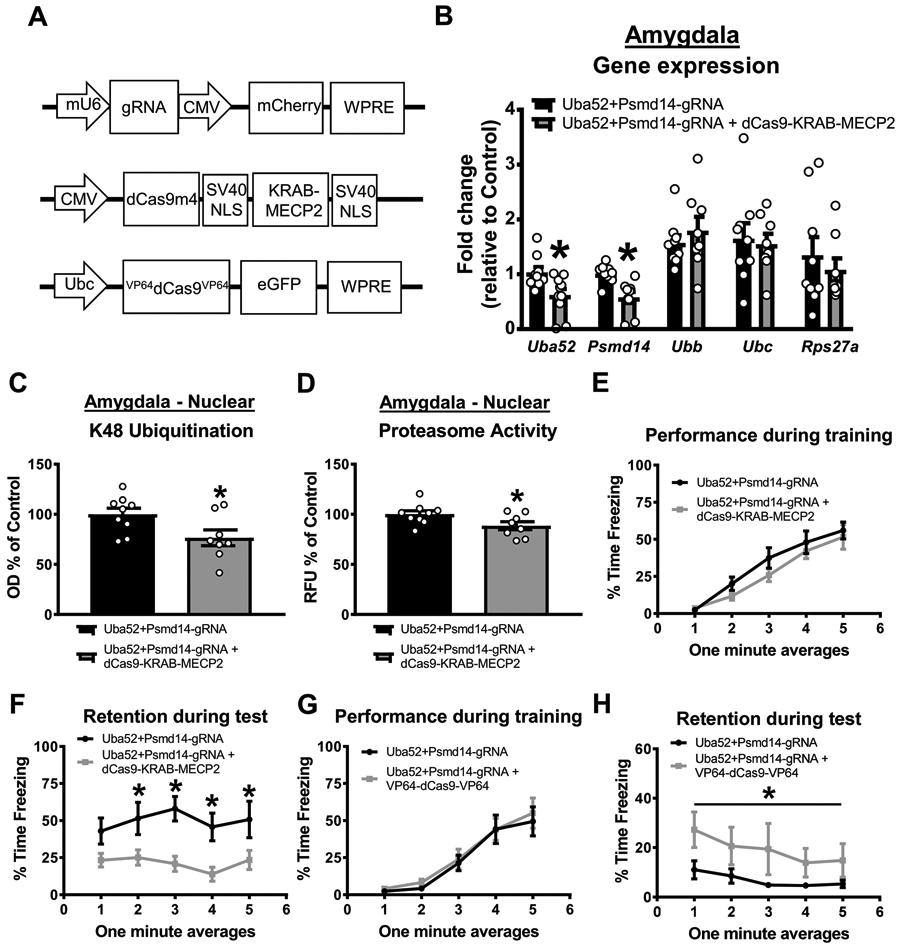
Female rats received basolateral amygdala (BLA) injections of CRISPR guide RNA (gRNA) targeting the ubiquitin coding gene Uba52 and proteasome subunit Psmd14 with or without dCas9-KRAB-MECP2 or VP64-dCas9-VP64 fusion. Two weeks later, animals were trained and tested on a contextual fear conditioning paradigm. (A) Schematic of the gRNA (bottom), dCas9-KRAB-MECP2 fusion (middle) or VP64-dCas9-VP64 fusion. (B) Two weeks after co-infusion of gRNA and dCas9-KRAB-MECP2 there was reduced expression of Uba52 and Psmd14, but not Ubb, Ubc or Rps27a, gene expression in the BLA (n = 9-10 per group). (C-D) This decreases in gene expression correlated with reduced K48 polyubiquitination (C) and proteasome activity (D) in the BLA (n = 8-9 per group). (E-F) Co-infusion of gRNA and dCas9-KRAB-MECP2 did not impair performance during the fear conditioning task (E) but significantly impaired long-term memory when tested the following day (F; n = 9-10 per group). (G-H) Female rats received basolateral amygdala (BLA) injections of CRISPR gRNA targeting the ubiquitin coding gene Uba52 and proteasome subunit Psmd14 with or without the VP64-dCas9-VP64 transcriptional activator fusion. Two weeks later, animals were trained and tested to a weak contextual fear conditioning paradigm in which the shock intensity was lowered to 0.6mA (still receiving 4 shocks). Co-infusion of gRNA and VP64-dCas9-VP64 did not alter performance during the fear conditioning task (G) but significantly enhanced long-term memory during the test session the following day (H; n = 8 per group). Line denotes that the average freezing across the entire testing session (all minutes summed) was significantly different between groups. * p < 0.05 from Uba52+Psmd14-gRNA.
