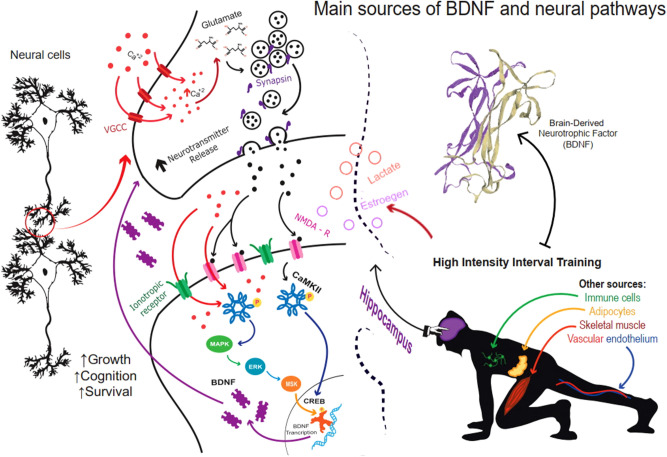
Figure 5.
Interval training increases circulating BDNF levels in healthy adults (upper right). During this response, the brain (hippocampal region) seems be the main BDNF source; nevertheless, other tissues function as BDNF synthesizers. The mechanism of activation during IT has not elucidated yet (above right). In brain, BDNF synthesis is activated by an increase of calcium (Ca2+) concentrations in the cytosol. Inside neurons, Ca2+ activates calmodulin dependent kinase II (CaMKII), triggering activation of the MAPK/ERK/MSK cascade resulting in an increase in the expression and phosphorylation of cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB). CREB initiates BDNF transcription resulting in increased BDNF synthesis and release (left). Once secreted, the neurotrophin regulates molecular mechanisms associated with neuronal growth, cognition, and neuron survival (above left). Finally, scientific evidence suggests that other circulating molecules such as lactate and estrogen enhance BDNF synthesis in brain (center). The putative mechanism indicate that lactate increases calcium current in the neurons, and estrogens activates nuclear estrogen receptors and membrane estrogen receptors that enhance the BDNF synthesis. Figure made with adobe illustrator cs6. https://www.adobe.com/products/illustrator/free-trial-download.html. Figure conceived and designed for PCGS.