FIGURE 5.
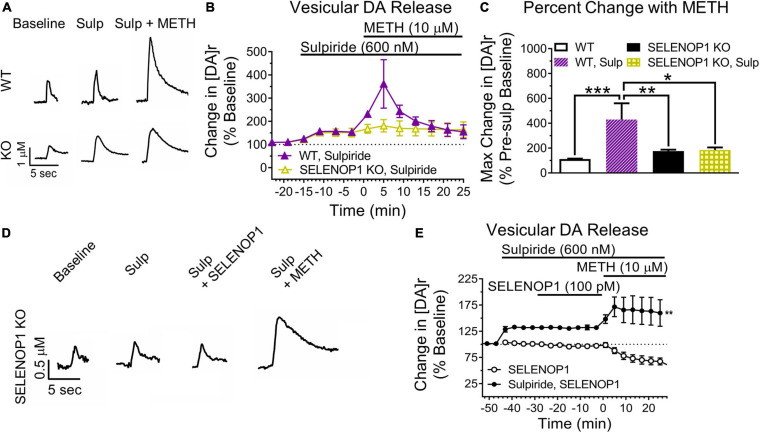
D2R antagonism unmasked elevated vesicular DA release in WT while preventing rescue in KO mice. (A) shown are sample traces showing sulpiride (Sulp; 600 nM) reduction of D2R auto-inhibition and subsequent responses to 10 μM methamphetamine (METH). (B) sulpiride increased the baseline evoked DA release from baseline values in WT and SELENOP1 KO mice similarly (148.5 ± 4.6% and 139.8 ± 6.1%, respectively; n = 4, 7; p = 0.4). (C) sulpiride caused a dramatic increase in [DA]r in WT mice (429.3 ± 131.4%; n = 3; One-way ANOVA: F(3,17) = 10.72; Tukey’s *p = 0.0111, **p = 0.0027, ***p = 0.002), while resulting in no changes to subsequent methamphetamine responses in SELENOP1 KO mice (176.3 ± 10.4%; n = 6) compared to the SELENOP1 KO methamphetamine responses without sulpiride (171.9 ± 1.86%; n = 6). Data are expressed relative to baseline values before sulpiride application and compared to non-sulpiride methamphetamine experiment responses. Values shown here for WT and SELENOP1 KO groups without sulpiride are the same data previously shown in Figure 3C. (D) SELENOP1 KO mouse sample DA traces following application of sulpiride and SELENOP1 protein prior to methamphetamine. (E) sulpiride prevented SELENOP1 protein from suppressing the methamphetamine-induced increase in [DA]r in SELENOP1 KO mice (203.4 ± 23.9%; One-way ANOVA: F(3,17) = n = 4; **p = 0.0069). All values reported are mean ± SEM.