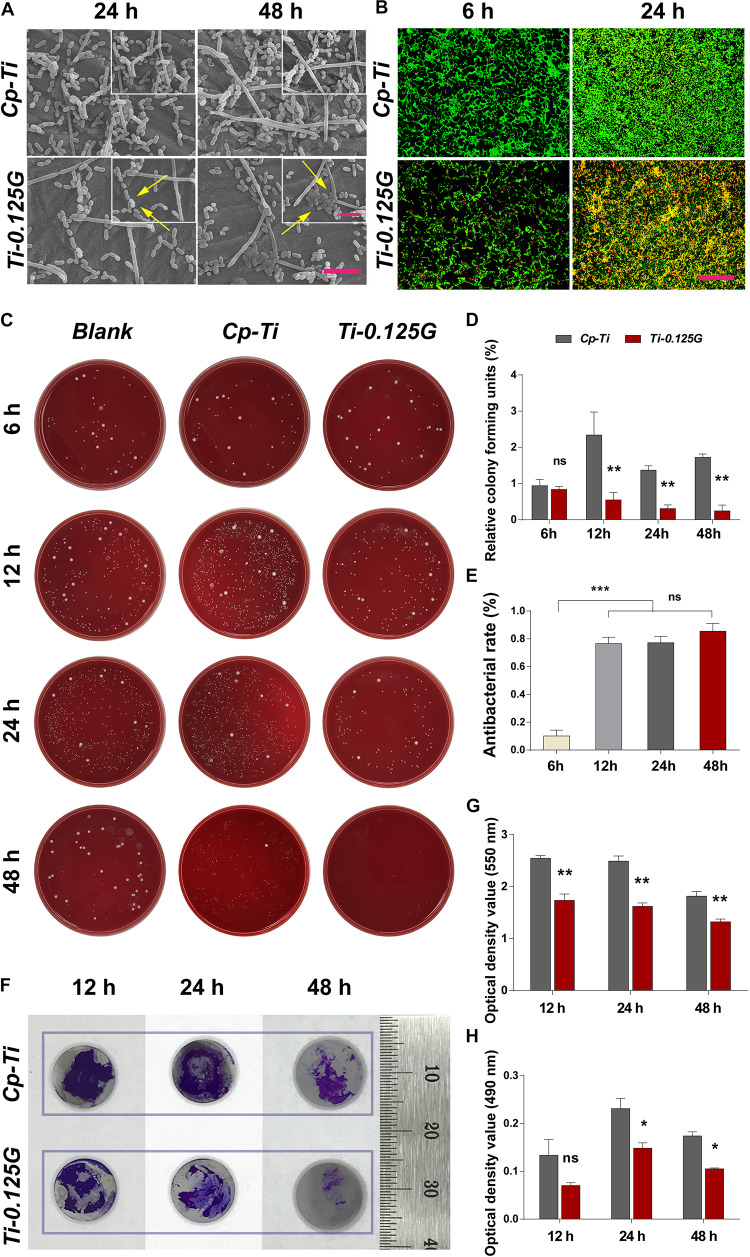
FIGURE 2.
The effects of samples against bacterial multispecies. (A) SEM micrographs of multiple bacteria on different samples after 24 and 48 h of incubation. Scale bar = 5 μm. The top right corner insert showed high magnification images (abnormal shapes of microbes were marked by white arrows). Scale bar for inserts = 2 μm. (B) CLSM images of bacterial multispecies cultured on different samples for 6 and 24 h. All microbial cells were stained with two well-described probes, interpreting live bacteria (green) and dead ones (red). Scale bar = 50 μm. (C) Typical images of re-cultured pathogens (containing S. mutans, F. nucleatum, and P. gingivalis) colonies on each substrate after 6, 12, 24, and 48 h of incubation. (D) and (E) Statistical results of relative CFUs and antibacterial rates of all groups. Noted that Ti-0.125G was the most effective in anti-bacteria after 6 h of interaction. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. (F) Measurements of biofilm’s biomass by CV staining at 12, 24, and 48 h of incubation. Scale bar was supplemented. (G) The statistical analysis noted that Ti-0.125G significantly inhibited bacterial multispecies biofilm. **p < 0.01. (H) Statistical analysis of MTT assay noted that Ti-0.125G reduced the viability of bacterial biofilms after 24 and 48 h of incubation. *p < 0.05.