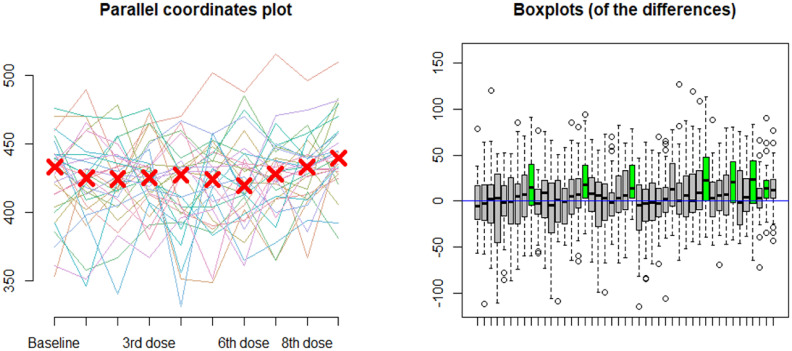
Fig. 3.
Differences in telemetry-measured QTc values with serial doses of hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin in COVID-19 patients (n = 68).
Left) Parallel coordinates plot for telemetry-measured QTc at baseline and following each drug dose administration in COVID-19 patients. Right) Post-hoc analysis of Friedman rank sum tests of repeated measures of QTc with serial drug dose administration. The X-axis represents the dose considered and the Y-axis represents the difference between the measured QTc between the two considered doses. The box plot indicates the distribution of differences between repeated measures of QTc with serial doses of hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin. As indicated by the green box plots from left to right, there were statistically significant differences between QTc measurements after the 9th dose when compared with baseline (p = 0.02) and following the 1st (p = 0.004), 2nd (p = 0.004), 4th (p = 0.006), 5th (p = 0.01), 6th (p = 0.02), and 7th (p = 0.02) doses, separately.