Table 1.
The examples of organic components commonly added during plastics manufacturing, their role and influence on living organisms (chemical structure figures were taken from ChemSpider: http://www.chemspider.com).
| Compound | Structure | Negative effect | Organism | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasticizers | ||||
| dimethyl phthalate (DMP) | 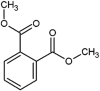 |
Oxidative damages, disturb of the gene expression levels | Zebrafish (Danio rerio) | (Cong et al., 2020) |
| inhibited growth, cell inactivation, cell membranes damage | Escherichia coli K12 | (Wang et al., 2019b) | ||
| prenatal exposure affects reproductive development | Human males | (Suzuki et al., 2012) | ||
| diethyl phthalate (DEP) | 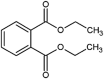 |
Reduced the average lifespan, decreased reproduction | Caenorhabditis elegans | (Pradhan et al., 2018) |
| histological structures damages of liver and kidneys, inhibition of cell proliferation | Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) | (Xiao et al., 2018) | ||
| diethylhexyl phthalate (DEHP) | 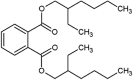 |
Liver damage, ROS generation, lipid peroxidation, immunosuppression | Catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco) | (Mo et al., 2019) |
| reduced the average lifespan, decreased reproduction | Caenorhabditis elegans | (Pradhan et al., 2018) | ||
| disruption of female fertility, hormones and ovarian folliculogenesis | Mice | (Chiang et al., 2020, Chiang and Flaws, 2019) | ||
| utero exposure decreases anogenital distance and reproductive, poses reproductive hazard | Human males | (Dorman et al., 2019) | ||
| diisodecyl phthalate (DIDP) | 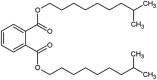 |
Behavioral, enzymological, and oxidative stress, disruption in circadian rhythm | Zebrafish (Danio rerio) | (Poopal et al., 2020) |
| liver and kidney damage, increase in levels of ROS | Balb/c mice | (Chen et al., 2019b) | ||
| diheptyl phthalate (DHP) | 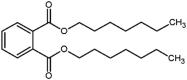 |
Behavioral, enzymological, and oxidative stress, disruption in circadian rhythm | Zebrafish (Danio rerio) | (Poopal et al., 2020) |
| diisononyl phthalate (DINP) | 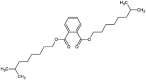 |
Accumulation of ROS, damage and inflammatory responses in liver and kidney tissues, neuroinflammation in the brain, disruption of female fertility, disruption of hormones and ovarian folliculogenesis | Mice | (Chiang et al., 2020, Duan et al., 2018, Ma et al., 2014) |
| decrease of testosterone level in male | Human | (Henrotin et al., 2020) | ||
| adversely affect oocytes growth and maturation, abnormal gonadal development and reproduction, disruption of the endocannabinoid system | Zebrafish (Danio rerio) | (Forner-Piquer et al., 2018, Santangeli et al., 2017) | ||
| Flame retardants | ||||
| tris(2-chloroethyl) phosphate (TCEP) | 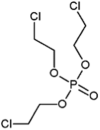 |
Influence on biochemical and electrolyte levels of fish, histopathological anomalies in the gills, liver, and kidney tissues | Freshwater fish (Cirrhinus mrigala) | (Sutha et al., 2020) |
| neurotoxicity by increasing thyroid hormones, induce of oxidative damage | Kunming mice | (Wang et al., 2020a) | ||
| down regulation of the expression of selected genes and proteins related to neurodevelopment of zebrafish embryos/larvae | Zebrafish | (Li et al., 2019) | ||
| tris(1-chloro-2-propyl)phosphate (TCPP) | 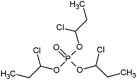 |
Significant alterations of proteins associated with: neurotransmission, neurodevelopment, signal transduction, transport, metabolism, and detoxification | Rockfish (Sebastes schlegeli) | (Ji et al., 2020) |
| tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA) | 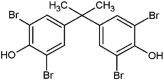 |
Affects the exploratory and anxiety-related behavior | Wistar rats | (Rock et al., 2019) |
| changes in thyroid receptor and deiodinase enzyme expression | Zebrafish (Danio rerio) | (Parsons et al., 2019) | ||
| Decabromodiphenyl ethane (DBDPE) | 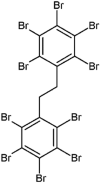 |
Induced oxidative stress, lipid membrane peroxidation, DNA damage | Earthworms (Eisenia fetida) | (Zhao et al., 2020) |
| induction of oxidative stress and an inflammation response resulted in endothelial dysfunction and cardiovascular disorders, could impair liver structure and function | Rats | (Jing et al., 2019, Sun et al., 2020) | ||
| Decabromodiphenyl ether (DBDE) | 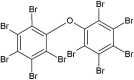 |
Disruption of molting, neurotoxicity (disruption of neurotransmitter signaling pathways) | Folsomia candida | (Zhang and Qiao, 2020) |
| adverse effect on phagocytosis of haemocytes, histopathological effects in gills | Marine scallop (Chlamys farreri) | (Xia et al., 2020) | ||
| Hexabromocyclododecane (HBCDD) | 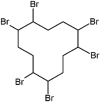 |
Developmental neurotoxicant, impairments in motor maturation of pups | Wistar rats | (Maurice et al., 2015) |
| induction of nuclear abnormalities | Benthic clams Macoma balthica (L.) | (Smolarz and Berger, 2009) | ||
| Antioxidants | ||||
| 3-t-butyl-4-hydroxyanisole (BHA) | 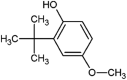 |
Stimulating action on ROS production | Rat liver | (de Oliveira Pateis et al., 2018) |
| butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) | 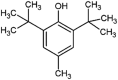 |
Cardiotoxicity, developmental toxicity | Zebrafish (Danio rerio) | (Sarmah et al., 2020) |
| Stabilizers | ||||
| bisphenol A (BPA) | 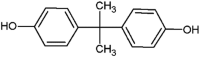 |
Developmental exposure lead to acute metabolic effects in larvae, affected hatchability and heart rates, craniofacial deformity, elongation of head length | Zebrafish (Danio rerio) | (Huang et al., 2020b, Martínez et al., 2020) |
| physiological and biochemical alterations, decrease in growth and vitality, increase in intracellular ROS level | Chlamydomonas reinhardtii Corbicula fluminea | (Esperanza et al., 2020) | ||
| Nonylphenol | 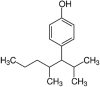 |
Impairing of germ cell development and maintenance the induction of the ROS leading to disruption of cell membrane and damages of cellular metabolism perinatally exposition causes myelination in the cerebellum of offspring | Mice | (Park et al., 2020) |
| Mullets (Liza klunzingeri) | (Salamat and Derakhshesh, 2020) | |||
| Wistar rats | (Jiang et al., 2020) | |||
ROS – reactive oxygen species.
