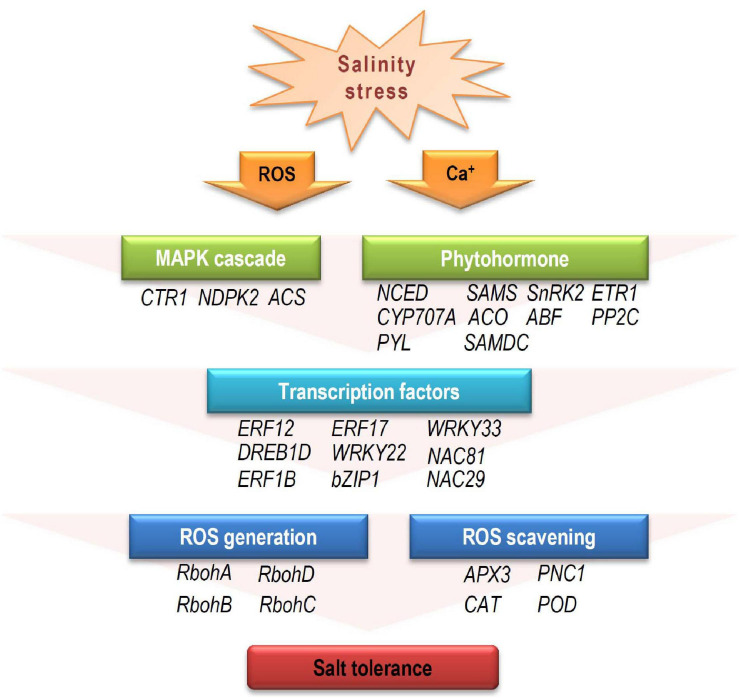
FIGURE 8.
The potential response model to salinity stress in cotton during early developmental stage. When exposed to salinity stress, the resultant stress signal alters secondary messengers, such as calcium (Ca2+), ROS, and stress hormones (ABA and ET). Downstream MAPK cascades influence expression of TFs (e.g., AP2/ERF, MYB, NAC, WRKY, and bZIP) that regulate target gene expression. These target genes are involved in ROS generation and scavenging, leading to varying salinity-stress responses. CTR1, constitutive triple response 1; NDPK2, nucleoside diphosphate kinase 2; ACS, 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid synthase; NCED, 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase; SAMS, s-adenosylmethionine synthase; SnRK2, sucrose nonfermenting 1 (SNF1)-related protein kinase 2; ETR1, ethylene response 1; CYP707A, cytochrome p450 family 707A; ACO, 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate oxidase 1; ABF, ABRE-binding factor; PP2C, protein phosphatases 2C; PYL, pyrabactin resistance1/PYR1-likes; SAMDC, s-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase proenzyme; RbohA-D, respiratory burst oxidase homologs A-D; APX3, ascorbate peroxidase 3; PNC1, cationic peroxidase 1; CAT, catalase; POD, peroxidase.