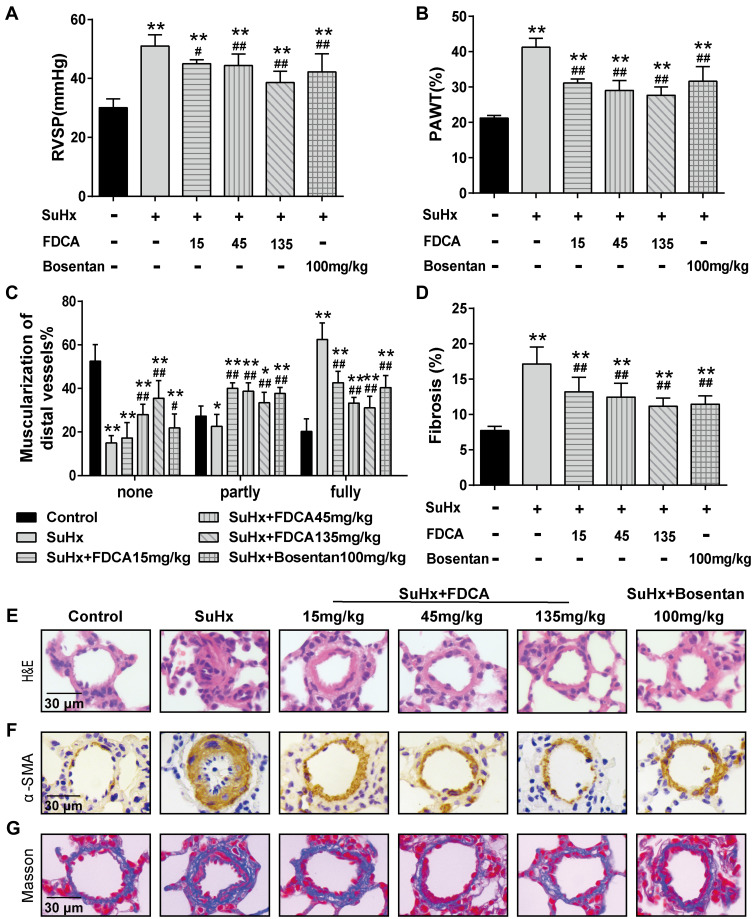
Figure 1.
FDCA attenuated hemodynamics and pulmonary vascular remodeling in the SU5416 plus hypoxia (SuHx)-induced rat model of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). (A) Hemodynamics were assessed based on right ventricular systolic pressure (RVSP). (B) Degree of pulmonary vascular remodeling was evaluated based on the pulmonary arterial wall thickness (PAWT). (C) Muscularization of distal pulmonary arteries was defined based on the proportion of alpha smooth muscle actin (α-SMA)-positive sites of circumference in PA medial wall: non-muscularized (none): ≤25%, partly muscularized (partly): 25–75%, and fully muscularized (fully): ≥75%. (D) Degree of pulmonary vascular adventitial fibrosis was evaluated based on the percentage of the collagen-positive area. (E) Representative images of hematoxylin-eosin (H&E) staining. (F) Representative images of immunohistochemical staining with α-SMA antibody (stained brown). (G) Representative images of Masson’s trichrome staining (collagen is stained blue) of lung sections. Data are expressed as mean ± SD (n=6-8). *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs normoxia control group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs SuHx group.