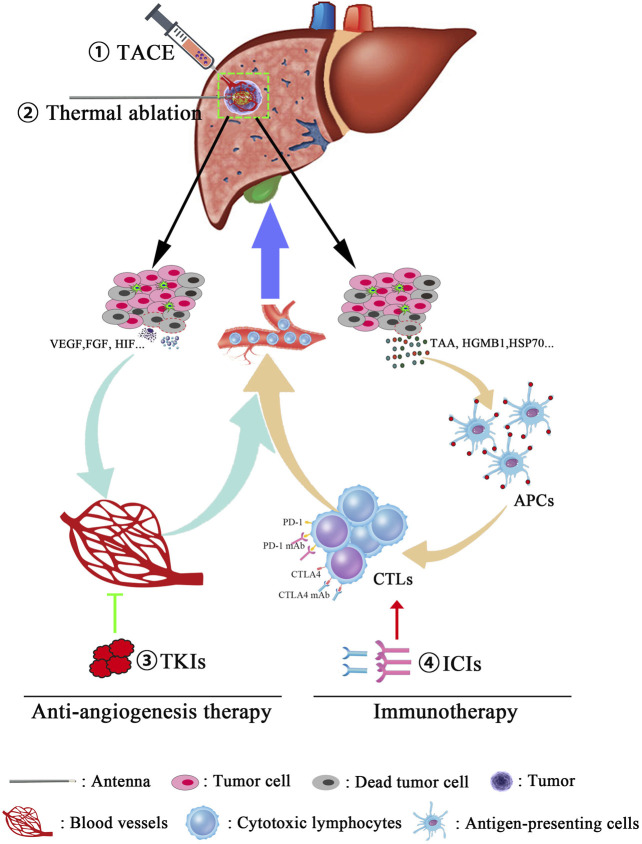
FIGURE 1.
Combination therapies for the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Multitreatment modalities were used for managing tumor progress, and the detailed procedures are also described as follows: First, for the purpose of tumor burden reduction, the cancerous blood supply was obstructed using transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE). Then, microwave ablation will further promote the tumor destruction in a manner of inducing an irreversible heat injury. Third, due to the necrosis and apoptosis of cancer cells, tumor-associated antigens (TAAs) and some cytokines such as VEGF, HIF, and FGF will be released into circulation, following an acute antitumor immune reaction and proangiogenic effects, respectively. Finally, immune checkpoint inhibitors (anti-PD1 mAb and anti-CTLA4 mAb) were used in order to remove the inhibition of antitumor effects and enhance the tumor-killing ability of CTLs. Moreover, antiangiogenesis therapy restrains the formation of blood vessels and leads to vascular normalization, which, in turn, synergically increases the infiltrated frequency of CTLs in tumor lesions.