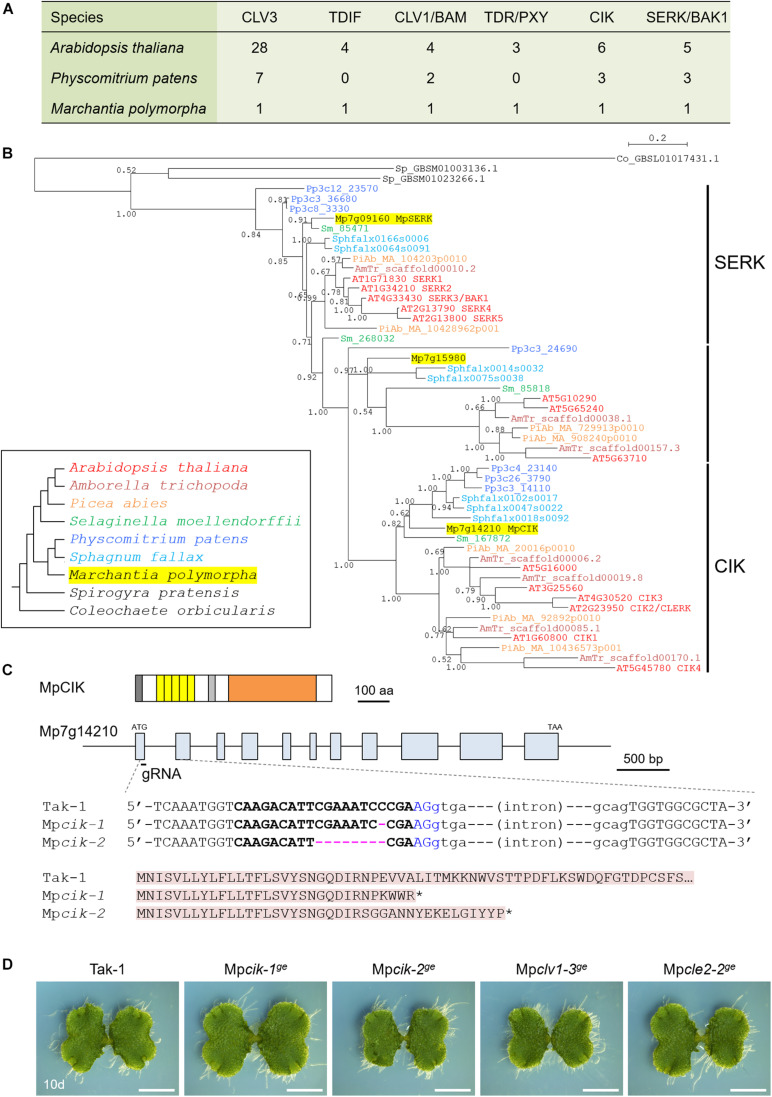
FIGURE 1.
Analysis of LRR-RLK subclass II in Marchantia polymorpha. (A) The number of CLE-receptor homologs. (B) A phylogenetic tree of subclass-II LRR-RLKs, generated with a Bayesian method based on the conserved kinase domain. The posterior probabilities of trees are shown at the nodes. Coleochaete sequence was used as an outgroup. Land plant sequences form a monophyletic clade, which can be divided into three subgroups as indicated on the right. Inset shows the list of species with their phylogenetic relationships. (C) Gene/protein structures and genome editing alleles of MpCIK. (top) Protein structure of MpCIK. (middle) Structure of MpCIK/Mp7g14210 locus with the position of a designed guide RNA (gRNA). (bottom) Genotyping of genome editing alleles. Target guide sequence is in bold and PAM sequence is in blue. Deleted bases are indicated with hyphens in magenta. Exon and intron are indicated in capital and small letters, respectively. N-terminal region of WT and mutant proteins deduced from the genomic DNA sequences are indicated below. Asterisks indicate translational termination. (D) Overall morphology of 10-day-old plants grown from gemmae. Scale bars represent 0.5 mm.