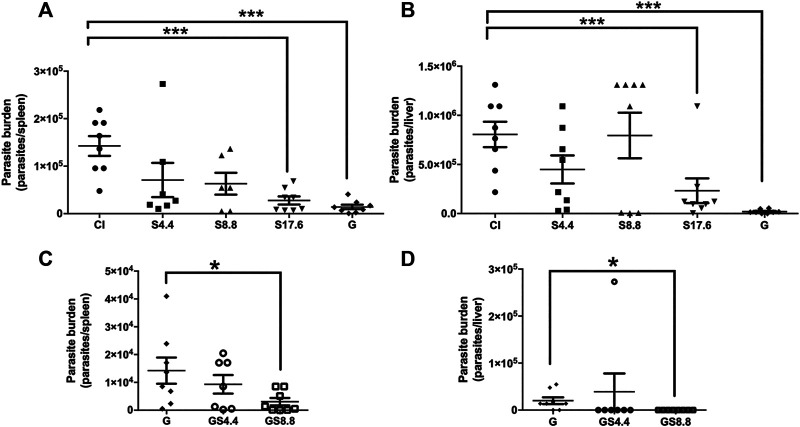
FIGURE 3.
Efficacy of oral spironolactone alone (A,B) and its association with meglumine antimoniate (C,D) in Experimental Visceral Leishmaniasis. BALB/c mice (8 per group) were infected intraperitoneally with 1.0 × 108 promastigotes of stationary phase L. infantum. Seven days after infection, the animals were treated with spironolactone in three different doses of 4.4, 8.8, and 17.6 mg/kg/day along with meglumine antimoniate (28 mg/kg/day of Sb5+) by intraperitoneal route. The control group was treated with the vehicle via an oral route (PBS containing 2% DMSO). Regarding the association between spironolactone and meglumine antimoniate, a fixed dose of meglumine antimoniate (28 mg/kg/day of Sb5+) was used with 4.4 or 8.8 mg/kg/day of spironolactone. After 23 days of treatment, the animals were euthanized in a CO2 chamber, and the spleen (panels A and C) and liver (panels B and D) were aseptically removed, weighed, and homogenized. The parasite load was estimated using the limiting dilution assay. Data are presented as means ± standard error of 8 animals per group; *p < 0.05 and ***p < 0.001; CI: control infected; S: spironolactone; and G: meglumine antimoniate.