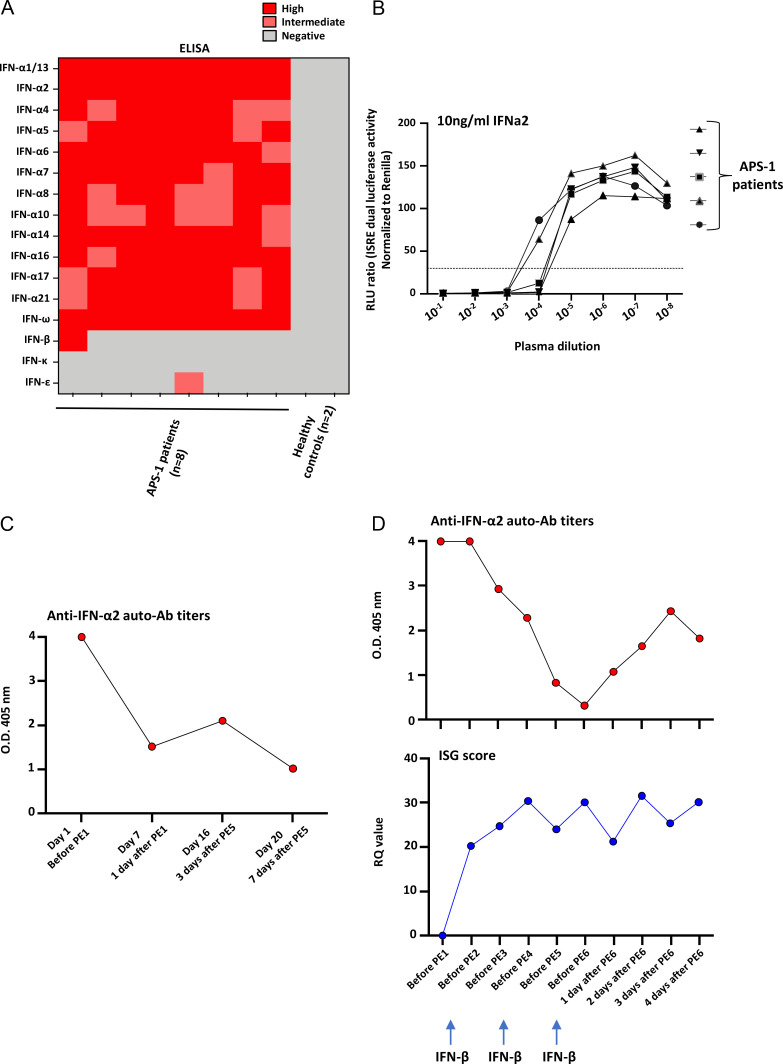
Figure 1.
APS-1 patients have neutralizing auto-Abs against type I IFNs, the titers of which can be decreased by plasmapheresis. (A) Titers of auto-Ab titers against the 17 type I IFNs in APS-1 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 (n = 8). (B) Neutralization of IFN-α2 by various dilutions of auto-Ab–containing serum from APS-1 patients with COVID-19 (n = 5). Relative luciferase activity is shown after stimulation with 10 ng/ml of IFN-α2. Results representative of two independent experiments are shown. ISRE, IFN stimulation response element; RLU, relative light units. (C) Plasmapheresis decreased the titers of type I IFN auto-Abs in one APS-1 patient (patient 17) with COVID-19 pneumonia. The titers of auto-Abs against IFN-α2 are shown for one of the APS-1 patients treated by plasmapheresis (PE). (D) Plasmapheresis (PE) decreased the titers of type I IFN auto-Abs in another APS-1 patient (patient 18) with COVID-19 pneumonia, treated with plasmapheresis, convalescent plasma, and IFN-β (as shown with arrows). The titers of auto-Abs against IFN-α2 are shown for the APS-1 patients treated by plasmapheresis in the upper panel. In the lower panel, ISG scores (evaluated by NanoString) show an increase after the initiation of treatments. ISG score cutoff for positivity is 2,758. RQ, relative quantitation.