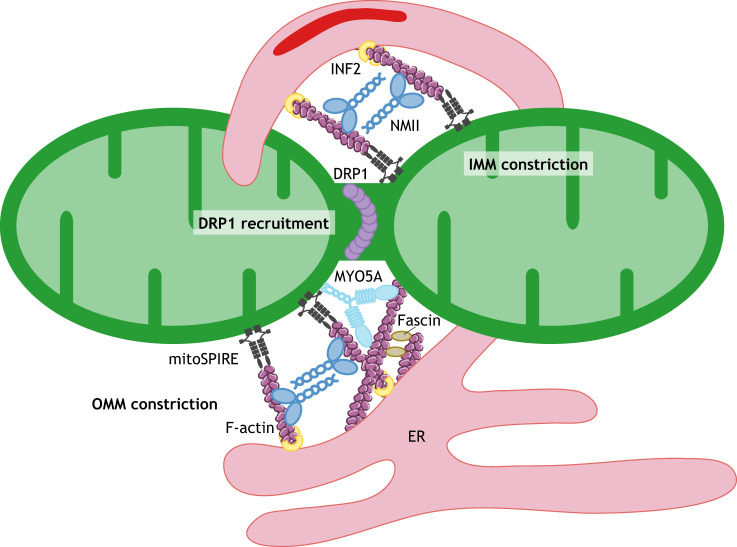
Fig. 2.
Motor proteins and cytoskeletal machinery regulating mitochondrial fission. Under steady-state conditions, the dynamic assembly of actin filaments onto mitochondria occurs at ER–mitochondria contact sites. Here, increased mitochondrial matrix Ca2+ activates the ER-bound formin INF2, resulting in actin polymerization. NMIIA provides the force to draw the ER and mitochondria closer together. At these ER–mitochondria contact sites, Ca2+ is transferred from the ER to mitochondria, triggering IMM constriction through an as-yet-unknown mechanism. Recruitment of the fission factor DRP1 from the cytosol to mitochondria involves several motor proteins (not shown). INF2 cooperates with mitoSPIRE and the actin bundling-protein fascin to drive polymerization of actin filaments on the mitochondrial surface, which target DRP1 to mitochondrial fission sites and stimulate its oligomerization. MYO5A, which interacts with mitoSPIRE, is recruited adjacent to DRP1 on mitochondria and facilitates fission; however, the exact role of MYO5A and actin filaments in this process remains to be established. Finally, NMII accumulates at mitochondrial constriction sites enabling DRP1 oligomerization and, by pulling actin filaments, provides the force for mitochondrial constriction. Actin filament images are adapted from Servier Medical Art (https://smart.servier.com/) under the terms of a CC-BY 3.0 license.