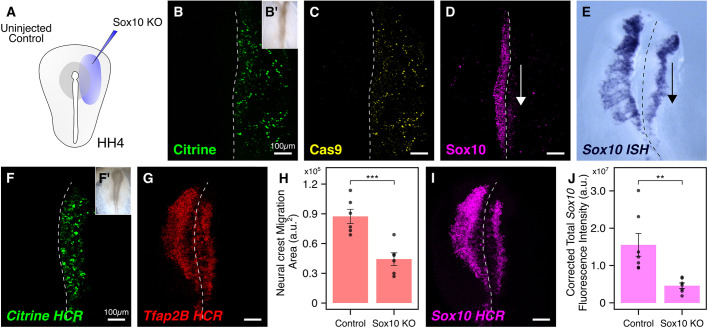
Fig. 3.
Electroporation-mediated early knockout of Sox10 using a single CRISPR plasmid. (A) Electroporation strategy to target Sox10 in the neural crest. The right side of gastrula-stage HH4 embryos was electroporated with a single CRISPR plasmid containing validated gRNA protospacer. (B-C) Embryos electroporated with the knockout construct developed to HH9 (B′) and immunostained for the expression of Citrine (B) and Cas9 (C). (D) The single-plasmid approach efficiently reduced Sox10 protein levels in emigrating cranial neural crest cells at HH9. (E) Chromogenic in situ hybridization (ISH) revealed a notable reduction in Sox10 mRNA levels in migrating cranial neural crest cells on the knockout side at HH9+. (F-J) Knockout embryos (F′) were processed for in situ HCR against Citrine (F), Tfap2B (G) and Sox10 (I). Quantification of migration area (H) and Sox10 fluorescence intensity (J) showed significant reduction in total area occupied by cranial neural crest cells (H; paired Student's t-test, ***P<0.001, n=6), and Sox10 mRNA levels (J; paired Student's t-test, **P<0.01, n=7) following single-CRISPR-plasmid-mediated Sox10 knockout. a.u., arbitrary units. Error bars represent s.e.m. Dashed line in image panels marks the midline.