Figure.
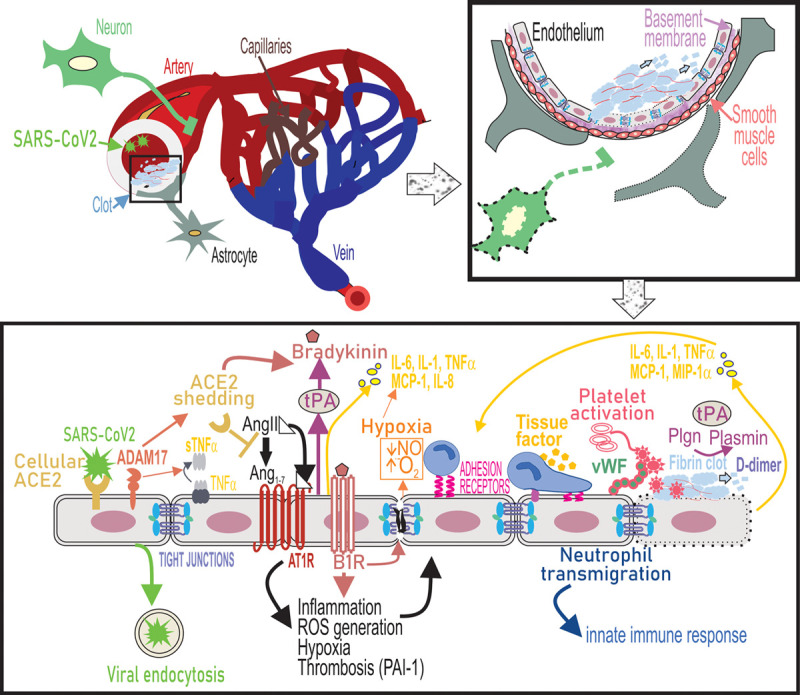
Endothelial dysfunction underlies cerebrovascular complications of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV2) infection. SARS-CoV2 binds to ACE2 receptors on the endothelial cells of large arteries and is endocytosed into the brain. Simultaneously, upregulation of ADAM17 (ADAM metallopeptidase domain 17) leads to shedding of ACE2 (angiotensin-converting enzyme 2) from the cell surface and as a result cell-bound ACE2-mediated conversion of Ang II (angiotensin II) to Ang1-7 is lost. ADAM-17 also functions as a TNF-α (tumor necrosis factor-α), convertase to release soluble TNF-α. Ang II binds to Ang II type 1 receptor (AT1R) and activation of AT1R triggers a range of intracellular cytokine signaling processes that lead to increased ROS generation and suppressed nitric oxide (NO) production from the endothelium, which causes vasoconstriction and potentiates oxidative stress causing endothelial activation. ACE2 depletion increases levels of bioactive bradykinin metabolite and binding of bradykinin to B2 receptors on endothelial cells promotes endothelial tight junction disruption. Ang II-AT1R signaling promotes gene expression of inflammatory cytokines including IL (interleukin)-6, TNF-α, MCP (monocyte chemoattractant protein)-1, and IL-8 via NF-κB signaling. Loss of ACE2 and therefore accumulation of AngII also induces tissue factor (TF) and PAI-1 (plasminogen activator inhibitor-1) expression by endothelial cells causes a shift in the PAI-1/tPA (tissue-type plasminogen activator) balance to a prothrombotic state. Endothelial activation also leads to upregulation of leukocyte adhesion molecules including VCAM-1 (vascular cell adhesion molecule), which promotes neutrophil transmigration. Hypoxia, cytokine activation, and oxidative stress promote platelet activation and release of VWF (von Willebrand Factor), which culminates in the formation of a fibrin clot on the endothelial cell surface. Fibrin in turn provides a cofactor for tPA-driven plasminogen activation that results in plasmin formation. Plasmin also cleaves the bradykinin precursor to yield bradykinin. These events trigger a thromboinflammatory loop that further causes endothelial dysfunction, leading to cerebrovascular pathologies. MIP-1α indicates macrophage inflammatory protein.
